boundary2, in association with The Social Life of Poetic Language conference at UCLA, is privileged to present a talk led by Rob Wilson.
-
The Mouse That Roared: The Democratic Movement in Hong Kong
an essay by Arif Dirlik
~
In 1997, the British government handed Hong Kong over to the People’s Republic of China(PRC) after 150 years of colonial rule. Some observers at the time could not but wonder if Hong Kong would be absorbed and remade by the behemoth to the north, or transform with its proverbial dynamism “the motherland” that already was undergoing radical change. The popular uprising under way in Hong Kong is the most recent indication that the question was not an idle one. The answer is yet to come.Hong Kong investments and technology played an important part in the 1980s in laying the ground for the PRC’s economic take-off. The “special economic zones” that were set up in Guangdong province at the beginning of “reform and opening” as gateways to global capitalism (while keeping the rest of the country immune to its effects) were intended to take advantage of the dynamic capitalism of neighboring Hong Kong. And they did. To this day, Guangdong leads the rest of the country in industrial production and wealth. It also heavily resembles Hong Kong with which it shares a common language and, despite three decades of separation after 1949, common cultural characteristics. Hong Kong has continued to play a crucial part in the country’s development.
It has been a different matter politically. Since the take-over in 1997 the leadership in Beijing has left no doubt of its enthusiasm for the oligarchic political structure that was already in place before the end of colonial rule. The many freedoms and rule of law Hong Kong people enjoyed were less appealing to a regime that preferred a population obedient to its strictures and a legal system more pliable at the service of Communist Party power. Already in the 1980s, Hong Kong people’s doubts about unification with the “motherland” were obvious in the exodus of those who could afford to leave to places like the United States, Canada and Australia. The exodus speeded up following the Tiananmen tragedy in 1989 which put to rest any hopes that reforms might open up a greater space for political freedoms. The colony practically disqualified itself as any kind of political inspiration for the Mainland with the enthusiastic participation of Hong Kongers in the Tiananmen movement leading up to the June Fourth massacre, and annual commemorations thereafter of the suppression of the student movement. In the early 1990s the Party under Deng Xiaoping settled on the example of Singapore as a model more attuned to its own authoritarian practices.
The same reasons that made the regime suspicious of Hong Kong people for their “lack of patriotism” due to the legacies of colonialism have made Hong Kong into an inspiration as well as a base for radical critics of the regime struggling for greater freedom and democracy on the Mainland. The take-over of 1997 was under the shadow of Tinanmen, but even so few would have imagined at the time that within two decades of the celebrations of the end of colonialism and “return” to the motherland, protestors against Beijing “despotism” would be waving British flags. Once the initial enthusiasm for “liberation” was over, Hong Kongers rediscovered as the source of their “difference” the colonial history which in nationalist historiography appeared as a lapse in the nation’s historical, a period of humiliation remembered most importantly to foster nationalist sentiment. PRC democracy activists such as the jailed Nobel Prize winner Liu Xiaobo have drawn the ire of the regime for suggesting that Hong Kong’s freedoms and democratic sentiments were legacies of colonial acculturation that Mainlanders had missed out on.
Current protests have their origins in a consciousness born of the anxieties provoked by the prospect of unification in the 1980s and 1990s, and even though both the Mainland and Hong Kong have changed radically in the intervening period, the Hong Kong identity that assumed recognizable contours at the time is a fundamental driving force of the protests. The immediate issue that has provoked the protests—call for universal suffrage in the selection of the chief executive and legislative council of the Special Administrative Region—harks back to the Basic Law of 1984 agreed upon by the British and the PRC as a condition of unification. The Basic Law stipulated that Hong Kong would be subject internally to its own laws for fifty years after the take-over under a system of “one country, two systems,” with its own chief executive and a legislature elected by an election committee representing various functional constituencies in a corporatist arrangement. The arrangement openly favored the corporate and financial ruling class in Hong Kong which in turn was prepared to align its interests with those of the Communist regime in a mutually beneficial relationship. The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (SAR) was something of a political counterpart to the “special economic zones”—an exception that was granted not to compromise national sovereignty but as an act of sovereign power. In all matters pertaining to governance and the law, the SAR would be accountable to the National People’s Congress (NPC) in Beijing. Hong Kong was granted representation in the NPC which, like all representation in that body, has served more to consolidate central control than to allow for the democratic airing of public opinion and grievances.
“One country, two systems” was an unstable structure. It was important to the PRC for patriotic reasons to put an end to the colonialism at its doorstep and retrieve territory lost a century and a half ago. But some compromise with the departing British was unavoidable given the strategic importance to the new project of development of the global corporate and financial hub that was Hong Kong. The autonomy granted to Hong Kong was subject to the good faith of the Beijing government. What might happen if the PRC no longer needed this hub seemed like a remote contingency in the 1980s, but already by the 1990s there was talk of the rise of Shanghai as a competitor. It is not out of the question that the present unrest which may undermine faith in Hong Kong as a corporate and financial center is not entirely undesirable to the regime now that preparations have been completed to launch a new financial center in Shanghai.
A similar uncertainty attended the issue of governance under the system. The Basic Law held out the possibility of democratic government and universal suffrage in Hong Kong subject to circumstances to be determined by the NPC. It nourished hopes in democracy, but reserved for Beijing final say on when and how democracy was to be exercised. There were no guarantees that full democracy would be granted if Hong Kongers invited the displeasure of the government in Beijing—or circumstances within the country made it undesirable. This is the immediate issue in the current protests (along with public dissatisfaction with the current chief executive, Leung Chun Ying who, like his two predecessors since 1997, is widely viewed as a Beijing puppet). To Hong Kong democracy advocates, the offer of universal suffrage is a mockery of the promise of full democracy when the choices are limited to candidates carefully selected by an electoral commission packed with Beijing loyalists.
The take-over in 1997, and the circumstances of its negotiation, had one very significant consequence that in likelihood was unanticipated: the politicization of Hong Kong society. Hong Kong long had a reputation as a cultural and political “desert.” The British colonial regime was successful in diverting popular energies to the struggle for everyday existence, and for those who could, the pursuit of wealth. At the height of the Cultural Revolution on the Mainland in 1967, labor disputes erupted into riots against the colonial government led by pro-Beijing leftists. But sustained political activity dates back to the negotiations surrounding the take-over, especially the mobilization instigated by the Tiananmen movement in Beijing. Politics over the last twenty-five years has revolved around the assertion of a Hong Kong identity against dissolution into the PRC. As a new political consciousness has found expression in the efflorescence of a Hong Kong culture in film and literature, the latter has played no little part in stimulating political activity. Ironically, while the goal of “one country, two systems” was to ease Hong Kong into the PRC, the very recognition of the differences of Hong Kong from the rest of the country would seem to have underlined the existence of a Hong Kong identity that differentiated the former colony from the rest of PRC society.
Current protests have focused attention on issues of governance. Far more important are the social tensions and the economic transformations that lend urgency to protestors’ demand for political recognition and rights. One important indication is the part young people—teenagers—have played in the protests. Joshua Wong, who has emerged as a leader, is seventeen years old, which means that he was born in 1997, the year of the take-over.
The generation Wong represents has come of age in a society subject to deepening social and economic problems. The wealth gap in Hong Kong is nothing new, but as elsewhere in the world, inequality has assumed critical proportions with increased concentration of wealth in the hands of the elite allied with Beijing. Since 1997, the experience of marginalization has been intensified with the inundation of the city by Mainlanders with their newfound wealth which has increased prices of commodities, put pressures on public services––including housing, health and education––and introduced new cultural fissures. Some Hong Kong businesses prefer Mainland customers on whose business they have come to be dependent. In the 1990s, Mainlanders living in Hong Kong used to complain about the prejudice they suffered from Hong Kongers with their pretensions to superior cultural sophistication. That has been reversed. Even the most uncouth Mainlanders are likely to look down on Hong Kongers for not being authentically Chinese, which typifies PRC attitudes toward Chinese populations elsewhere. While Hong Kongers complain about “locusts” from the North, a very-unConfucian Beijing University professor descended from Confucius refers to Hong Kongers as “bastards” contaminated by their colonial past. The central government in Beijing, sharing the suspicious of southerners of its imperial predecessors, is engaged in efforts to discourage the use of Cantonese while instilling in the local population its version of what it means to be “Chinese.” We may recall that the present protests were preceded two years ago by successful protests against Beijing-backed efforts to introduce “patriotic” education to Hong Kong schools. It is not that Hong Kong people are not patriotic. They are very patriotic indeed. But their patriotism is mediated by their Hong Kong identity, a very product of the take-over that Beijing would like to erase.
The upheaval in Hong bears similarities to “Occupy” movements elsewhere in the economic issues that inform it. It also has its roots in the special circumstances of Hong Kong society, and its relationship to Beijing. The movement may be viewed as the latest chapter in a narrative that goes back to the 1980s, the emergence of a neoliberal global capitalism of which the PRC has been an integral component, and the Tiananmen movement which was one of the earliest expressions of the social and political strains created by shifts in the global economy. The demands for democracy in the protests are clearly not merely “political.” Democracy is important to the protestors not only as a means to retrieving some control over their lives, but also to overcome inequality. The authorities in Beijing are quite aware of this link. A Law professor from Tsinghua University in Beijing who also serves as an advisor on Hong Kong affairs just recently announced that democracy would jeopardize the wealthy who are crucial to the welfare of Hong Kong’s capitalist economy. It may seem ironic that a Communist Party should be devoted to the protection of wealthy capitalists, but that is the reality of contemporary PRC society that the protestors are struggling against.
The protests are also the latest chapter in the formation of a Hong Kong identity which assumed urgency with the prospect of return to the “motherland” in the 1980s. This, too, is a threat to a regime in flux that finds itself threatened by identity claims among the populations it rules over. It seems superfluous to say that allowing the people of Hong Kong the self-rule they demand would have adverse consequences in encouraging separatism among the various ethnic groups already in rebellion against the regime, and further stimulate democracy activists among the Han population. Hitherto pro-Beijing Guomindang leader in Taiwan, Ma Ying-jeou, has recently voiced his opposition to unification under the “one country, two-systems” formula.
It would probably take something of a miracle for the protest movement in Hong Kong to achieve its stated goals. Rather than risk a Tiananmen style confrontation, the authorities have taken a wait-and-see attitude, waiting for the movement to spend its force, or opponents to force it to retreat. There are signs already that the movement has run its course in clashes between the protestors and members of the general public weary of the disruption of life and business. It is suspected that the attackers included members of Triad gangs. Whom they might be serving is, for the moment, anybody’s guess.
What the next chapter might bring is uncertain, to say the least. It is unlikely that a movement that has been in the making for two decades will simply fade away into oblivion. The problems it set out to resolve are very real, and offer little sign of resolution, and the movement has proven its resilience through the years. The distinguished scholar of Hong Kong-Mainland relations at the City University of Hong Kong, Joseph Cheng Yu-shek,who is also an advocate of democracy, stated in a recent interview that, “All the protesters here and Hong Kong people know it is extremely unlikely the Chinese leaders will respond to our demands…. We are here to say we are not going to give up, we will continue to fight on. We are here because as long as we fight on, at least we haven’t lost.”
-
"Malaysia's Dog Issue" by b2 writer Masturah Alatas
Masturah Alatas, a boundary 2 contributor, has written about the ‘I want to touch a dog’ event in Malaysia for CounterPunch. You can read “Malaysia’s Dog Issue” here.
-
Arne De Boever joins b2 as Advisory Editor
boundary 2 is proud and honored to announce that Arne De Boever has become an Advisory Editor.
Arne De Boever works on contemporary American fiction and critical theory and teaches at the California Institute of the Arts, where he also directs the MA Aesthetics and Politics program. His books include States of Exception in the Contemporary Novel and Narrative Care: Biopolitics and the Novel.
-

Frank Pasquale — Capital’s Offense: Law’s Entrenchment of Inequality (On Piketty, “Capital in the 21st Century”)
a review of Thomas Piketty, Capital in the Twenty-First Century (Harvard University Press, 2014)
~
Thomas Piketty’s Capital in the Twenty-First Century has succeeded both commercially and as a work of scholarship. Capital‘s empirical research is widely praised among economists—even by those who disagree with its policy prescriptions. It is also the best-selling book in the century-long history of Harvard University Press, and a rare work of scholarship to reach the top spot on Amazon sales rankings.[1]
Capital‘s main methodological contribution is to bring economic, sociological, and even literary perspectives to bear in a work of economics.[2] The book bridges positive and normative social science, offering strong policy recommendations for increased taxation of the wealthiest. It is also an exploration of historical trends.[3] In Capital, fifteen years of careful archival research culminate in a striking thesis: capitalism exacerbates inequality over time. There is no natural tendency for markets themselves, or even ordinary politics, to slow accumulation by top earners.[4]
This review explains Piketty’s analysis and its relevance to law and social theory, drawing lessons for the re-emerging field of political economy. Piketty’s focus on long-term trends in inequality suggests that many problems traditionally explained as sector-specific (such as varied educational outcomes) are epiphenomenal with regard to increasingly unequal access to income and capital. Nor will a narrowing of purported “skills gaps” do much to improve economic security, since opportunity to earn money via labor matters far less in a world where capital is the key to enduring purchasing power. Policymakers and attorneys ignore Piketty at their peril, lest isolated projects of reform end up as little more than rearranging deck chairs amidst titanically unequal opportunities.
Inequality, Opportunity, and the Rigged Game
Capital weaves together description and prescription, facts and values, economics, politics, and history, with an assured and graceful touch. So clear is Piketty’s reasoning, and so compelling the enormous data apparatus he brings to bear, that few can doubt he has fundamentally altered our appreciation of the scope, duration, and intensity of inequality.[5]
Piketty’s basic finding is that, absent extraordinary political interventions, the rate of return on capital (r) is greater than the rate of growth of the economy generally (g), which Piketty expresses via the now-famous formula r > g.[6] He finds that this relationship persists over time, and in the many countries with reliable data on wealth and income.[7] This simple inequality relationship has many troubling implications, especially in light of historical conflicts between capital and labor.
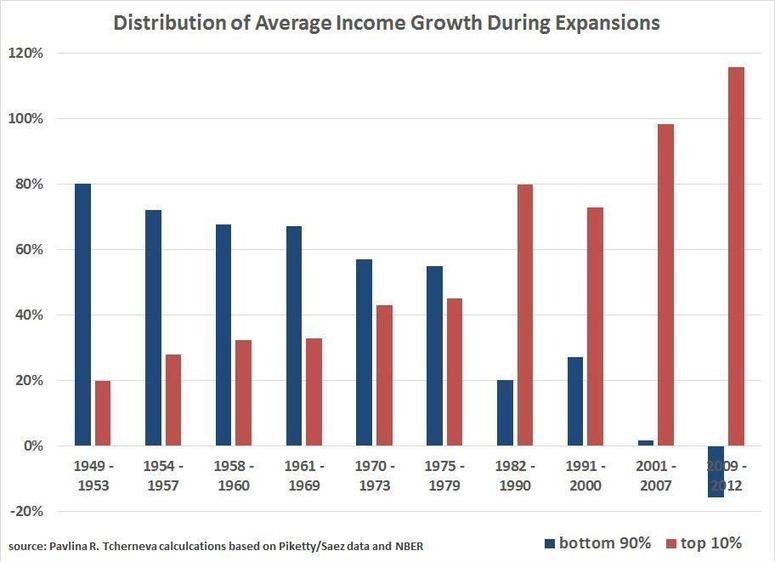
Most persons support themselves primarily by wages—that is, what they earn from their labor. As capital takes more of economic output (an implication of r > g persisting over time), less is left for labor. Thus if we are concerned about unequal incomes and living standards, we cannot simply hope for a rising tide of growth to lift the fortunes of those in the bottom quintiles of the income and wealth distribution. As capital concentrates, its owners take an ever larger share of income—unless law intervenes and demands some form of redistribution.[8] As the chart below (by Bard economist Pavlina Tcherneva, based on Piketty’s data) shows, we have now reached the point where the US economy is not simply distributing the lion’s share of economic gains to top earners; it is actively redistributing extant income of lower decile earners upwards:
In 2011, 93% of the gains in income during the economic “recovery” went to the top 1%. From 2009 to 2011, “income gains to the top 1% … were 121% of all income increases,” because “incomes to the bottom 99% fell by 0.4%.”[9] The trend continued through 2012.
Fractal inequality prevails up and down the income scale.[10] The top 15,000 tax returns in the US reported an average taxable income of $26 million in 2005—at least 400 times greater than the median return.[11] Moreover, Larry Bartels’s book, Unequal Democracy, graphs these trends over decades.[12] Bartels shows that, from 1945-2007, the 95th percentile did much better than those at lower percentiles.[13] He then shows how those at the 99.99th percentile did spectacularly better than those at the 99.9th, 99.5th, 99th, and 95th percentiles.[14] There is some evidence that even within that top 99.99th percentile, inequality reigned. In 2005, the “Fortunate 400″—the 400 households with the highest earnings in the U.S.—made on average $213.9 million apiece, and the cutoff for entry into this group was a $100 million income—about four times the average income of $26 million prevailing in the top 15,000 returns.[15] As Danny Dorling observed in a recent presentation at the RSA, for those at the bottom of the 1%, it can feel increasingly difficult to “keep up with the Joneses,” Adelsons, and Waltons. Runaway incomes at the very top leave those slightly below the “ultra-high net worth individual” (UHNWI) cut-off ill-inclined to spread their own wealth to the 99%.
Thus inequality was well-documented in these, and many other works, by the time Piketty published Capital—indeed, other authors often relied on the interim reports released by Piketty and his team of fellow inequality researchers over the past two decades.[16] The great contribution of Capital is to vastly expand the scope of the inquiry, over space and time. The book examines records in France going back to the 19th century, and decades of data in Germany, Japan, Great Britain, Sweden, India, China, Portugal, Spain, Argentina, Switzerland, and the United States.[17]
The results are strikingly similar. The concentration of capital (any asset that generates income or gains in monetary value) is a natural concomitant of economic growth under capitalism—and tends to intensify if growth slows or stops.[18] Inherited fortunes become more important than those earned via labor, since the “miracle of compound interest” overwhelms any particularly hard-working person or ingenious idea. Once fortunes grow large enough, their owners can simply live off the interest and dividends they generate, without ever drawing on the principal. At the “escape velocity” enjoyed by some foundations and ultra-rich individuals, annual expenses are far less than annual income, precipitating ever-greater principal. This is Warren Buffett’s classic “snowball” of wealth—and we should not underestimate its ability to purchase the political favors that help constitute Buffettian “moats” around the businesses favored by the likes of Berkshire-Hathaway.[19] Dynasties form and entrench their power. If they can make capital pricey enough, even extraordinary innovations may primarily benefit their financers.
Deepening the Social Science of Political Economy
Just as John Rawls’s Theory of Justice laid a foundation for decades of writing on social justice, Piketty’s work is so generative that one could envision whole social scientific fields revitalized by it.[20] Political economy is the most promising, a long tradition of (as Piketty puts it) studying the “ideal role of the state in the economic and social organization of a country.”[21] Integrating the long-divided fields of politics and economics, a renewal of modern political economy could unravel “wicked problems” neither states nor markets alone can address.[22]
But the emphasis in Piketty’s definition of political economy on “a country,” versus countries, or the world, is in tension with the global solutions he recommends for the regulation of capital. The dream of neoliberal globalization was to unite the world via markets.[23] Anti-globalization activists have often advanced a rival vision of local self-determination, predicated on overlaps between political and economic boundaries. State-bound political economy could theorize those units. But the global economy is, at present, unforgiving of autarchy and unlikely to move towards it.
Capital tends to slip the bonds of states, migrating to tax havens. In the rarefied world of the global super-rich, financial privacy is a purchasable commodity. Certainly there are always risks of discovery, or being taken advantage of by a disreputable tax shelter broker or shady foreign bank. But for many wealthy individuals, tax havenry has been a rite of passage on the way to membership in a shadowy global elite. Piketty’s proposed global wealth tax would need international enforcement—for even the Foreign Accounts Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) imposed via America’s fading hegemony (and praised by Piketty) has only begun to address the problem of hidden (or runaway) wealth (and income).[24]
It will be very difficult to track down the world’s hidden fortunes and tax them properly. Had Piketty consulted more legal sources, he may have acknowledged the problem more adequately in Capital. He recommends “automatic information exchange” among tax authorities, which is an excellent principle to improve enforcement. But actually implementing this principle could require fine-grained regulation of IT systems, deployment of whole new types of surveillance, and even uniform coding (via, say, standard legal entity identifiers, or LEIs) globally. More frankly acknowledging the difficulty of shepherding such legislation globally could have led to a more convincing (and comprehensive) examination of the shortcomings of globalized capitalism.
In several extended interviews on Capital (with CNN Money, Econtalk, The New York Times, Huffington Post, and the New Republic, among others), Piketty pledges fealty to markets, praising their power to promote production and innovation. Never using the term “industrial policy” in his book, Piketty hopes that law may make the bounty of extant economic arrangements accessible to all, rather than changing the nature of those arrangements. But we need to begin to ask whether our very process of creating goods and services itself impedes better distribution of them.
Unfortunately, mainstream economics itself often occludes this fundamental question. When distributive concerns arise, policymakers can either substantively intervene to reshape the benefits and burdens of commerce (a strategy economists tend to derogate as dirigisme), or may, post hoc, use taxes and transfer programs to redistribute income and wealth. For establishment economists, redistribution (happening after initial allocations by “the market”) is almost always considered more efficient than “distortion” of markets by regulation, public provision, or “predistribution.”[25]
Tax law has historically been our primary way of arranging such redistribution, and Piketty makes it a focus of the concluding part of his book, called “Regulating Capital.” Piketty laments the current state of tax reporting and enforcement. Very wealthy individuals have developed complex webs of shell entities to hide their true wealth and earnings.[26] As one journalist observed, “Behind a New York City deed, there may be a Delaware LLC, which may be managed by a shell company in the British Virgin Islands, which may be owned by a trust in the Isle of Man, which may have a bank account in Liechtenstein managed by the private banker in Geneva. The true owner behind the structure might be known only to the banker.”[27] This is the dark side of globalization: the hidden structures that shield the unscrupulous from accountability.[28]
The most fundamental tool of tax secrecy is separation: between persons and their money, between corporations and the persons who control them, between beneficial and nominal controllers of wealth. When money can pass between countries as easily as digital files, skilled lawyers and accountants can make it impossible for tax authorities to uncover the beneficial owners of assets (and the income streams generated by those assets).
Piketty believes that one way to address inequality is strict enforcement of laws like America’s FATCA.[29] But the United States cannot accomplish much without pervasive global cooperation. Thus the international challenge of inequality haunts Capital. As money concentrates in an ever smaller global “superclass” (to use David J. Rothkopf’s term), it’s easier for it to escape any ruling authority.[30] John Chung has characterized today’s extraordinary concentrations of wealth as a “death of reference” in our monetary system and its replacement with “a total relativity.”[31] He notes that “[i]n 2007, the average amount of annual compensation for the top twenty-five highest paid hedge fund managers was $892 million;” in the past few years, individual annual incomes in the group have reached two, three, or four billion dollars. Today’s greatest hoards of wealth are digitized, as easily moved and hidden as digital files.
We have no idea what taxes may be due from trillions of dollars in offshore wealth, or to what purposes it is directed.[32] In less-developed countries, dictators and oligarchs smuggle ill-gotten gains abroad. Groups like Global Financial Integrity and the Tax Justice Network estimate that illicit financial flows out of poor countries (and into richer ones, often via tax havens) are ten times greater than the total sum of all development aid—nearly $1 trillion per year. Given that the total elimination of extreme global poverty could cost about $175 billion per year for twenty years, this is not a trivial loss of funds—completely apart from what the developing world loses in the way of investment when its wealthiest residents opt to stash cash in secrecy jurisdictions.[33]
An adviser to the Tax Justice Network once said that assessing money kept offshore is an “exercise in night vision,” like trying to measure “the economic equivalent of an astrophysical black hole.”[34] Shell corporations can hide connections between persons and their money, between corporations and the persons who control them, between beneficial and nominal owners. When enforcers in one country try to connect all these dots, there is usually another secrecy jurisdiction willing to take in the assets of the conniving. As the Tax Justice Network’s “TaxCast” exposes on an almost monthly basis, victories for tax enforcement in one developed country tend to be counterbalanced by a slide away from transparency elsewhere.
Thus when Piketty recommends that “the only way to obtain tangible results is to impose automatic sanctions not only on banks but also on countries that refuse to require their financial institutions” to report on wealth and income to proper taxing authorities, one has to wonder: what super-institution will impose the penalties? Is this to be an ancillary function of the WTO?[35] Similarly, equating the imposition of a tax on capital with “the stroke of a pen” (568) underestimates the complexity of implementing such a tax, and the predictable forms of resistance that the wealth defense industry will engage in.[36] All manner of societal and cultural, public and private, institutions will need to entrench such a tax if it is to be a stable corrective to the juggernaut of r > g.[37]
Given how much else the book accomplishes, this demand may strike some as a cavil—something better accomplished by Piketty’s next work, or by an altogether different set of allied social scientists. But if Capital itself is supposed to model (rather than merely call for) a new discipline of political economy, it needs to provide more detail about the path from here to its prescriptions. Philosophers like Thomas Pogge and Leif Wenar, and lawyers like Terry Fisher and Talha Syed, have been quite creative in thinking through the actual institutional arrangements that could lead to better distribution of health care, health research, and revenues from natural resources.[38] They are not cited in Capital¸but their work could have enriched its institutional analysis greatly.
An emerging approach to financial affairs, known as the Legal Theory of Finance (LTF), also offers illumination here, and should guide future policy interventions. Led by Columbia Law Professor Katharina Pistor, an interdisciplinary research team of social scientists and attorneys have documented the ways in which law is constitutive of so-called financial markets.[39] Revitalizing the tradition of legal realism, Pistor has demonstrated the critical role of law in generating modern finance. Though law to some extent shapes all markets, in finance, its role is most pronounced. The “products” traded are very little more than legal recognitions of obligations to buy or sell, own or owe. Their value can change utterly based on tiny changes to the bankruptcy code, SEC regulations, or myriad other laws and regulations.
The legal theory of finance changes the dialogue about regulation of wealth. The debate can now move beyond stale dichotomies like “state vs. market,” or even “law vs. technology.” While deregulationists mock the ability of regulators to “keep up with” the computational capacities of global banking networks, it is the regulators who made the rules that made the instantaneous, hidden transfer of financial assets so valuable in the first place. Such rules are not set in stone.
The legal theory of finance also enables a more substantive dialogue about the central role of law in political economy. Not just tax rules, but also patent, trade, and finance regulation need to be reformed to make the wealthy accountable for productively deploying the wealth they have either earned or taken. Legal scholars have a crucial role to play in this debate—not merely as technocrats adjusting tax rules, but as advisors on a broad range of structural reforms that could ensure the economy’s rewards better reflected the relative contributions of labor, capital, and the environment.[40] Lawyers had a much more prominent role in the Federal Reserve when it was more responsive to workers’ concerns.[41]
Imagined Critics as Unacknowledged Legislators
A book is often influenced by its author’s imagined critics. Piketty, decorous in his prose style and public appearances, strains to fit his explosive results into the narrow range of analytical tools and policy proposals that august economists won’t deem “off the wall.”[42] Rather than deeply considering the legal and institutional challenges to global tax coordination, Piketty focuses on explaining in great detail the strengths and limitations of the data he and a team of researchers have been collecting for over a decade. But a renewed social science of political economy depends on economists’ ability to expand their imagined audience of critics, to those employing qualitative methodologies, to attorneys and policy experts working inside and outside the academy, and to activists and journalists with direct knowledge of the phenomena addressed. Unfortunately, time that could have been valuably directed to that endeavor—either in writing Capital, or constructively shaping the extraordinary publicity the book received—has instead been diverted to shoring up the book’s reputation as rigorous economics, against skeptics who fault its use of data.
To his credit, Piketty has won these fights on the data mavens’ own terms. The book’s most notable critic, Chris Giles at the Financial Times, tried to undermine Capital‘s conclusions by trumping up purported ambiguities in wealth measurement. His critique was rapidly dispatched by many, including Piketty himself.[43] Indeed, as Neil Irwin observed, “Giles’s results point to a world at odds not just with Mr. Piketty’s data, but also with that by other scholars and with the intuition of anyone who has seen what townhouses in the Mayfair neighborhood of London are selling for these days.”[44]
One wonders if Giles reads his own paper. On any given day one might see extreme inequality flipping from one page to the next. For example, in a special report on “the fragile middle,” Javier Blas noted that no more than 12% of Africans earned over $10 per day in 2010—a figure that has improved little, if at all, since 1980.[45] Meanwhile, in the House & Home section on the same day, Jane Owen lovingly described the grounds of the estate of “His Grace Henry Fitzroy, the 12th Duke of Grafton.” The grounds cost £40,000 to £50,000 a year to maintain, and were never “expected to do anything other than provide pleasure.”[46] England’s revanchist aristocracy makes regular appearances in the Financial Times “How to Spend It” section as well, and no wonder: as Oxfam reported in March, 2014, Britain’s five richest families have more wealth than its twelve million poorest people.[47]
Force and Capital
The persistence of such inequalities is as much a matter of law (and the force behind it to, say, disperse protests and selectively enforce tax regulations), as it is a natural outgrowth of the economic forces driving r and g. To his credit, Piketty does highlight some of the more grotesque deployments of force on behalf of capital. He begins Part I (“Income and Capital”) and ends Part IV (“Regulating Capital”) by evoking the tragic strike at the Lonmin Mine in South Africa in August 2012. In that confrontation, “thirty-four strikers were shot dead” for demanding pay of about $1,400 a month (there were making about $700).[48] Piketty deploys the story to dramatize conflict over the share of income going to capital versus labor. But it also illustrates dynamics of corruption. Margaret Kimberley of Black Agenda Report claims that the union involved was coopted thanks to the wealth of the man who once ran it.[49] The same dynamics shine through documentaries like Big Men (on Ghana), or the many nonfiction works on oil exploitation in Africa. [50]
Piketty observes that “foreign companies and stockholders are at least as guilty as unscrupulous African elites” in promoting the “pillage” of the continent.[51] Consider the state of Equatorial Guinea, which struck oil in 1995. By 2006, Equatoguineans had the third highest per capita income in the world, higher than many prosperous European countries.[52] Yet the typical citizen remains very poor. [53] In the middle of the oil boom, an international observer noted that “I was unable to see any improvements in the living standards of ordinary people. In 2005, nearly half of all children under five were malnourished,” and “[e]ven major cities lack[ed] clean water and basic sanitation.”[54] The government has not demonstrated that things have improved much since them, despite ample opportunity to do so. Poorly paid soldiers routinely shake people down for bribes, and the country’s president, Teodoro Obiang, has paid Moroccan mercenaries for his own protection. A 2009 book noted that tensions in the country had reached a boiling point, as the “local Bubi people of Malabo” felt “invaded” by oil interests, other regions were “abandoned,” and self-determination movements decried environmental and human rights abuses.[55]
So who did benefit from Equatorial Guinea’s oil boom? Multinational oil companies, to be sure, though we may never know exactly how much profit the country generated for them—their accounting was (and remains) opaque. The Riggs Bank in Washington, D.C. gladly handled accounts of President Obiang, as he became very wealthy. Though his salary was reported to be $60,000 a year, he had a net worth of roughly $600 million by 2011.[56] (Consider, too, that such a fortune would not even register on recent lists of the world’s 1,500 or so billionaires, and is barely more than 1/80th the wealth of a single Koch brother.) Most of the oil companies’ payments to him remain shrouded in secrecy, but a few came to light in the wake of US investigations. For example, a US Senate report blasted him for personally taking $96 million of his nation’s $130 million in oil revenue in 1998, when a majority of his subjects were malnourished.[57]
Obiang’s sordid record has provided a rare glimpse into some of the darkest corners of the global economy. But his story is only the tip of an iceberg of a much vaster shadow economy of illicit financial flows, secrecy jurisdictions, and tax evasion. Obiang could afford to be sloppy: as the head of a sovereign state whose oil reserves gave it some geopolitical significance, he knew that powerful patrons could shield him from the fate of an ordinary looter. Other members of the hectomillionaire class (and plenty of billionaires) take greater precautions. They diversify their holdings into dozens or hundreds of entities, avoiding public scrutiny with shell companies and pliant private bankers. A hidden hoard of tens of trillions of dollars has accumulated, and likely throws off hundreds of billions of dollars yearly in untaxed interest, dividends, and other returns.[58] This drives a wedge between a closed-circuit economy of extreme wealth and the ordinary patterns of exchange of the world’s less fortunate.[59]
The Chinese writer and Nobel Peace Prize winner Liu Xiaobo once observed that corruption in Beijing had led to an officialization of the criminal and the criminalization of the official.[60] Persisting even in a world of brutal want and austerity-induced suffering, tax havenry epitomizes that sinister merger, and Piketty might have sharpened his critique further by focusing on this merger of politics and economics, of private gain and public governance. Authorities promote activities that would have once been proscribed; those who stand in the way of such “progress” might be jailed (or worse). In Obiang’s Equatorial Guinea, we see similar dynamics, as the country’s leader extracts wealth at a volume that could only be dreamed of by a band of thieves.
Obiang’s curiously double position, as Equatorial Guinea’s chief law maker and law breaker, reflects a deep reality of the global shadow economy. And just as “shadow banks” are rivalling more regulated banks in terms of size and influence, shadow economy tactics are starting to overtake old standards. Tax avoidance techniques that were once condemned are becoming increasingly acceptable. Campaigners like UK Uncut and the Tax Justice Network try to shame corporations for opportunistically allocating profits to low-tax jurisdictions.[61] But CEOs still brag about their corporate tax unit as a profit center.
When some of Republican presidential candidate Mitt Romney’s recherché tax strategies were revealed in 2012, Barack Obama needled him repeatedly. The charges scarcely stuck, as Romney’s core constituencies aimed to emulate rather than punish their standard-bearer.[62] Obama then appointed a Treasury Secretary (Jack Lew), who had himself utilized a Cayman Islands account. Lew was the second Obama Treasury secretary to suffer tax troubles: Tim Geithner, his predecessor, was also accused of “forgetting” to pay certain taxes in a self-serving way. And Obama’s billionaire Commerce Secretary Penny Pritzker was no stranger to complex tax avoidance strategies.[63]
Tax attorneys may characterize Pritzker, Lew, Geithner, and Romney as different in kind from Obiang. But any such distinctions they make will likely need to be moral, rather than legal, in nature. Sure, these American elites operated within American law—but Obiang is the law of Equatorial Guinea, and could easily arrange for an administrative agency to bless his past actions (even developed legal systems permit retroactive rulemaking) or ensure the legality of all future actions (via safe harbors). The mere fact that a tax avoidance scheme is “legal” should not count for much morally—particularly as those who gain from prior US tax tweaks use their fortunes to support the political candidacies of those who would further push the law in their favor.
Shadowy financial flows exemplify the porous boundary between state and market. The book Tax Havens: How Globalization Really Works argues that the line between savvy tax avoidance and illegal tax evasion (or strategic money transfers and forbidden money laundering) is blurring.[64] Between our stereotypical mental images of dishonest tycoons sipping margaritas under the palm trees of a Caribbean tax haven, and a state governor luring a firm by granting it a temporary tax abatement, lie hundreds of subtler scenarios. Dingy rows of Delaware, Nevada, and Wyoming file cabinets can often accomplish the same purpose as incorporating in Belize or Panama: hiding the real beneficiaries of economic activity.[65] And as one wag put it to journalist Nicholas Shaxson, “the most important tax haven in the world is an island”—”Manhattan.”[66]
In a world where “tax competition” is a key to neoliberal globalization, it is hard to see how a global wealth tax (even if set at the very low levels Piketty proposes) supports (rather than directly attacks) existing market order. Political elites are racing to reduce tax liability to curry favor with the wealthy companies and individuals they hope to lure, serve, and bill. The ultimate logic of that competition is a world made over in the image of Obiang’s Equatorial Guinea: crumbling infrastructure and impoverished citizenries coexisting with extreme luxury for a global extractive elite and its local enablers. Books like Third World America, Oligarchy, and Captive Audience have already started chronicling the failure of the US tax system to fund roads, bridges, universal broadband internet connectivity, and disaster preparation.[67] As tax avoiding elites parley their gains into lobbying for rules that make tax avoidance even easier, self-reinforcing inequality seems all but inevitable. Wealthy interests can simply fund campaigns to reduce their taxes, or to reduce the risk of enforcement to a nullity. As Ben Kunkel pointedly asks, “How are the executive committees of the ruling class in countries across the world to act in concert to impose Piketty’s tax on just this class?”[68]
US history is instructive here. Congress passed a tax on the top 0.1% of earners in 1894, only to see the Supreme Court strike the tax down in a five to four decision. After the 16th Amendment effectively repealed that Supreme Court decision, Congress steadily increased the tax on high income households. From 1915 to 1918, the highest rate went from 7% to 77%, and over fifty-six tax brackets were set. When high taxes were maintained for the wealthy after the war, tax evasion flourished. At this point, as Jeffrey Winters writes, the government had to choose whether to “beef up law enforcement against oligarchs … , or abandon the effort and instead squeeze the same resources from citizens with far less material clout to fight back.”[69] Enforcement ebbed and flowed. But since then, what began by targeting the very wealthy has grown to include “a mass tax that burdens oligarchs at the same effective rate as their office staff and landscapers.”[70]
The undertaxation of America’s wealthy has helped them capture key political processes, and in turn demand even less taxation. The dynamic of circularity teaches us that there is no stable, static equilibrium to be achieved between regulators and regulated. The government is either pushing industry to realize some public values in its activities (say, by investing in sustainable growth), or industry is pushing its regulators to promote its own interests.[71] Piketty may worry that, if he too easily accepts this core tenet of politico-economic interdependence, he’ll be dismissed as a statist socialist. But until political economists do so, their work cannot do justice to the voices of those prematurely dead as a result of the relentless pursuit of profit—ranging from the Lonmin miners, to those crushed at Rana Plaza, to the spike of suicides provoked by European austerity and Indian microcredit gone wrong, to the thousands of Americans who will die early because they are stuck in states that refuse to expand Medicaid.[72] Contemporary political economy can only mature if capitalism’s ghosts constrain our theory and practice as pervasively as communism’s specter does.
Renewing Political Economy
Piketty has been compared to Alexis de Tocqueville: a French outsider capable of discerning truths about the United States that its own sages were too close to observe. The function social equality played in Tocqueville’s analysis, is taken up by economic inequality in Piketty’s: a set of self-reinforcing trends fundamentally reshaping the social order.[73] I’ve written tens of thousands of words on this inequality, but the verbal itself may be outmatched in the face of the numbers and force behind these trends.[74] As film director Alex Rivera puts it, in an interview with The New Inquiry:
I don’t think we even have the vocabulary to talk about what we lose as contemporary virtualized capitalism produces these new disembodied labor relations. … The broad, hegemonic clarity is the knowledge that a capitalist enterprise has the right to seek out the cheapest wage and the right to configure itself globally to find it. … The next stage in this process…is for capital to configure itself to enable every single job to be put on the global market through the network.[75]
Amazon’s “Mechanical Turk” has begun that process, supplying “turkers” to perform tasks at a penny each.[76] Uber, Lyft, TaskRabbit, and various “gig economy” imitators assure that micro-labor is on the rise, leaving micro-wages in its wake.[77] Workers are shifting from paid vacation to stay-cation to “nano-cation” to “paid time off” to hoarding hours to cover the dry spells when work disappears.[78] These developments are all predictable consequences of a globalization premised on maximizing finance rents, top manager compensation, and returns to shareholders.
Inequality is becoming more outrageous than even caricaturists used to dare. The richest woman in the world (Gina Rinehart) has advised fellow Australians to temper their wage demands, given that they are competing against Africans willing to work for two dollars day.[79] Or consider the construct of Dogland, from Korzeniewicz and Moran’s 2009 book, Unveiling Inequality:
The magnitude of global disparities can be illustrated by considering the life of dogs in the United States. According to a recent estimate … in 2007-2008 the average yearly expenses associated with owning a dog were $1425 … For sake of argument, let us pretend that these dogs in the US constitute their own nation, Dogland, with their average maintenance costs representing the average income of this nation of dogs.
By such a standard, their income would place Dogland squarely as a middle-income nation, above countries such as Paraguay and Egypt. In fact, the income of Dogland would place its canine inhabitants above more than 40% of the world population. … And if we were to focus exclusively on health care expenditures, the gap becomes monumental: the average yearly expenditures in Dogland would be higher than health care expenditures in countries that account for over 80% of the world population.[80]
Given disparities like this, wages cannot possibly reflect just desert: who can really argue that a basset hound, however adorable, has “earned” more than a Bangladeshi laborer? Cambridge economist Ha Joon Chang asks us to compare the job and the pay of transport workers in Stockholm and Calcutta. “Skill” has little to do with it. The former, drivers on clean and well-kept roads, may easily be paid fifty times more than the latter, who may well be engaged in backbreaking, and very skilled, labor to negotiate passengers among teeming pedestrians, motorbikes, trucks, and cars.[81]
Once “skill-biased technological change” is taken off the table, the classic economic rationale for such differentials focuses on the incentives necessary to induce labor. In Sweden, for example, the government assures that a person is unlikely to starve, no matter how many hours a week he or she works. By contrast, in India, 42% of the children under five years old are malnourished.[82] So while it takes $15 or $20 an hour just to get the Swedish worker to show up, the typical Indian can be motivated to labor for much less. But of course, at this point the market rationale for the wage differential breaks down entirely, because the background set of social expectations of earnings absent work is epiphenomenal of state-guaranteed patterns of social insurance. The critical questions are: how did the Swedes generate adequate goods and services for their population, and the social commitment to redistribution necessary in order to assure that unemployment is not a death sentence? And how can such social arrangements create basic entitlements to food, housing, health care, and education, around the world?
Piketty’s proposals for regulating capital would be more compelling if they attempted to answer questions like those, rather than focusing on the dry, technocratic aim of tax-driven wealth redistribution. Moreover, even within the realm of tax law and policy, Piketty will need to grapple with several enforcement challenges if a global wealth tax is to succeed. But to its great credit, Capital adopts a methodology capacious enough to welcome the contributions of legal academics and a broad range of social scientists to the study (and remediation) of inequality.[83] It is now up to us to accept the invitation, realizing that if we refuse, accelerating inequality will undermine the relevance—and perhaps even the very existence—of independent legal authority.
Frank Pasquale (@FrankPasquale) is a Professor of Law at the University of Maryland Carey School of Law. His forthcoming book, The Black Box Society: The Secret Algorithms that Control Money and Information (Harvard University Press, 2015), develops a social theory of reputation, search, and finance. He blogs regularly at Concurring Opinions. He has received a commission from Triple Canopy to write and present on the political economy of automation. He is a member of the Council for Big Data, Ethics, and Society, and an Affiliate Fellow of Yale Law School’s Information Society Project.
Back to the essay
_____[1] Dennis Abrams, Piketty’s “Capital”: A Monster Hit for Harvard U Press, Publishing Perspectives, at http://publishingperspectives.com/2014/04/pilkettys-capital-a-monster-hit-for-harvard-u-press/ (Apr. 29, 2014).
[2] Intriguingly, one leading economist who has done serious work on narrative in the field, Dierdre McCloskey, offers a radically different (and far more positive) perspective on the nature of economic growth under capitalism. Evan Thomas, Has Thomas Piketty Met His Match?, http://www.spectator.co.uk/features/9211721/unequal-battle/. But this is to be expected as richer methodologies inform economic analysis. Sometimes the best interpretive social science leads not to consensus, but to ever sharper disagreement about the nature of the phenomena it describes and evaluates. Rather than trying to bury normative differences in jargon or flatten them into commensurable cost-benefit calculations, it surfaces them.
[3] As Thomas Jessen Adams argues, “to understand how inequality has been overcome in the past, we must understand it historically.” Adams, The Theater of Inequality, at http://nonsite.org/feature/the-theater-of-inequality. Adams critiques Piketty for failing to engage historical evidence properly. In this review, I celebrate the book’s bricolage of methodological approaches as the type of problem-driven research promoted by Ian Shapiro.
[4] Thomas Piketty, Capital in the Twenty-First Century 17 (Arthur Goldhammer trans., 2014).
[5] Doug Henwood, The Top of the World, Book Forum, Apr. 2014, http://www.bookforum.com/inprint/021_01/12987; Suresh Naidu, Capital Eats the World, Jacobin (May 30, 2014), https://www.jacobinmag.com/2014/05/capital-eats-the-world/.
[6] Thomas Piketty, Capital in the Twenty-First Century 25 (Arthur Goldhammer trans., 2014).
[7] Id.
[8] As Piketty observes, war and revolution can also serve this redistributive function. Piketty, supra n. 3, at 20. Since I (and the vast majority of attorneys) do not consider violence a legitimate tool of social change, I do not include these options in my discussion of Piketty’s book.
[9] Frank Pasquale, Access to Medicine in an Era of Fractal Inequality, 19 Annals of Health Law 269 (2010).
[10] Charles R. Morris, The Two Trillion Dollar Meltdown: Easy Money, High Rollers, and the Great Credit Crash 139-40 (2009); see also Edward N. Wolff, Top Heavy: The Increasing Inequality of Wealth in America and What Can Be Done About It 36 (updated ed. 2002).
[11] Yves Smith, Yes, Virginia, the Rich Continue to Get Richer: The Top 1% Get 121% of Income Gains Since 2009, Naked Capitalism (Feb. 13, 2013), http://www.nakedcapitalism.com/2013/02/yes-virginia-the-rich-continue-to-get-richer-the-1-got-121-of-income-gains-since-2009.html#XxsV2mERu5CyQaGE.99.
[12] Larry M. Bartels, Unequal Democracy: The Political Economy of the New Gilded Age 8,10 (2010).
[13] Id. at 8.
[14] Id. at 10.
[15] Tom Herman, There’s Rich, and There’s the ‘Fortunate 400′, Wall St. J., Mar. 5, 2008, http://online.wsj.com/article/SB120468366051012473.html.
[16] See Thomas Piketty & Emmanuel Saez, The Evolution of Top Incomes: A Historical and International Perspective, 96 Am. Econ. Rev. 200, 204 (2006).
[17] Piketty, supra note 4, at 17. Note that, given variations in the data, Piketty is careful to cabin the “geographical and historical boundaries of this study” (27), and must “focus primarily on the wealthy countries and proceed by extrapolation to poor and emerging countries” (28).
[18] Id. at 46, 571 (“In this book, capital is defined as the sum total of nonhuman assets that can be owned and exchanged on some market. Capital includes all forms of real property (including residential real estate) as well as financial and professional capital (plants, infrastructure, machinery, patents, and so on) used by firms and government agencies.”).
[19] Alice Schroeder, The Snowball: Warren Buffett and the Business of Life (Bantam-Dell, 2008); Adam Levine-Weinberg, Warren Buffett Loves a Good Moat, at http://www.fool.com/investing/general/2014/06/30/warren-buffett-loves-a-good-moat.aspx.
[20] John Rawls, A Theory of Justice (1971).
[21] Piketty, supra note 4, at 540.
[22] Atul Gawande, Something Wicked This Way Comes, New Yorker (June 28, 2012), http://www.newyorker.com/news/daily-comment/something-wicked-this-way-comes.
[23] Philip Mirowski, Never Let a Serious Crisis Go to Waste: How Neoliberalism Survived the Financial Meltdown (2013).
[24] The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) was passed in 2010 as part of the Hiring Incentives to Restore Employment Act, Pub. L. No. 111-147, 124 Stat. 71 (2010), codified in sections 1471 to 1474 of the Internal Revenue Code, 26 U.S.C. §§ 1471-1474. The law is effective as of 2014. It requires foreign financial institutions (FFIs) to report financial information about accounts held by United States persons, or pay a withholding tax. Id.
[25] Christopher William Sanchirico, Deconstructing the New Efficiency Rationale, 86 Cornell L. Rev. 1003, 1005 (2001).
[26] Nicholas Shaxson, Treasure Islands: Uncovering the Damage of Offshore Banking and Tax Havens (2012); Jeanna Smialek, The 1% May be Richer than You Think, Bloomberg, Aug. 7, 2014, at http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-08-06/the-1-may-be-richer-than-you-think-research-shows.html (collecting economics research).
[27] Andrew Rice, Stash Pad: The New York real-estate market is now the premier destination for wealthy foreigners with rubles, yuan, and dollars to hide, N.Y. Mag., June 29, 2014, at http://nymag.com/news/features/foreigners-hiding-money-new-york-real-estate-2014-6/#.
[28] Ronen Palan, Richard Murphy, and Christian Chavagneux, Tax Havens: How Globalization Really Works 272 (2009) (“[m]ore than simple conduits for tax avoidance and evasion, tax havens actually belong to the broad world of finance, to the business of managing the monetary resources of individuals, organizations, and countries. They have become among the most powerful instruments of globalization, one of the principal causes of global financial instability, and one of the large political issues of our times.”).
[29] 26 U.S.C. § 1471-1474 (2012); Itai Grinberg, Beyond FATCA: An Evolutionary Moment for the International Tax System (Georgetown Law Faculty, Working Paper No. 160, 2012), available at http://scholarship.law.georgetown.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1162&context=fwps_papers.
[30] David Rothkopf, Superclass: The Global Power Elite and the World They Are Making (2009).
[31] John Chung, Money as Simulacrum: The Legal Nature and Reality of Money, 5 Hasting Bus. L.J. 109,149 (2009).
[32] James S. Henry, Tax Just. Network, The Price Of Offshore Revisited: New Estimates For “Missing” Global Private Wealth, Income, Inequality, And Lost Taxes 3 (2012), available at http://www.taxjustice.net/cms/upload/pdf/Price_of_Offshore_Revisited_120722.pdf; Scott Highman et al., Piercing the Secrecy of Offshore Tax Havens, Wash. Post (Apr. 6, 2013), http://www.washingtonpost.com/investigations/piercing-the-secrecy-of-offshore-tax-havens/2013/04/06/1551806c-7d50-11e2-a044-676856536b40_story.html.
[33] Dev Kar & Devon Cartwright‐Smith, Center for Int’l Pol’y, Illicit Financial Flows from Developing Countries: 2002-2006 (2012); Jeffrey Sachs, The End of Poverty: Economic Possibilities for Our Time (2006); Ben Harack, How Much Would it Cost to End Extreme Poverty in the World?, Vision Earth, (Aug. 26, 2011), http://www.visionofearth.org/economics/ending-poverty/how-much-would-it-cost-to-end-extreme-poverty-in-the-world/.
[34] Henry, supra note 68.
[35] Piketty, supra note 4, at 523.
[36] Jeffrey Winters coined the term “wealth defense industry” in his book, Oligarchy. See Frank Pasquale, Understanding Wealth Defense: Direct Action from the 0.1%, at http://www.concurringopinions.com/archives/2011/11/understanding-wealth-defense-direct-action-from-the-0-1.html.
[37] For a similar argument, focusing on the historical specificity of the US parallel to the trente glorieuses, see Thomas Jessen Adams, The Theater of Inequality, http://nonsite.org/feature/the-theater-of-inequality.
[38] Thomas Pogge, The Health Impact Fund: Boosting Pharmaceutical Innovation Without Obstructing Free Access, 18 Cambridge Q. Healthcare Ethics 78 (2008) (proposing global R&D fund);William Fisher III, Promise to Keep: Technology, Law, and the Future of Entertainment (2007); William W. Fisher & Talha Syed, Global Justice in Healthcare: Developing Drugs for the Developing World, 40 U.C. Davis L. Rev. 581 (2006).
[39] Katharina Pistor, A Legal Theory of Finance, 41 J. Comp. Econ. 315 (2013); Law in Finance, 41 J. Comp. Econ (2013). Several other articles in the same journal issue discuss the implications of LTF for derivatives, foreign currency exchange, and central banking.
[40] University of Chicago Law Professor Eric A. Posner and economist Glen Weyl recognize this in their review of Piketty, arguing that “the fundamental problem facing American capitalism is not the high rate of return on capital relative to economic growth that Piketty highlights, but the radical deviation from the just rewards of the marketplace that have crept into our society and increasingly drives talented students out of innovation and into finance.” Posner & Weyl, Thomas Piketty Is Wrong: America Will Never Look Like a Jane Austen Novel,” The New Republic, July 31, 2014, at http://www.newrepublic.com/article/118925/pikettys-capital-theory-misunderstands-inherited-wealth-today. See also Timothy A. Canova, The Federal Reserve We Need, 21 American Prospect 9 (October 2010), at http://prospect.org/article/federal-reserve-we-need.
[41] Timothy Canova, The Federal Reserve We Need: It’s the Fed We Once Had, at http://prospect.org/article/federal-reserve-we-need; Justin Fox, How Economics PhDs Took Over the Federal Reserve, at http://blogs.hbr.org/2014/02/how-economics-phds-took-over-the-federal-reserve/.
[42] Jack M. Balkin, From Off the Wall to On the Wall: How the Mandate Challenge Went Mainstream, Atlantic (June 4, 2012, 2:55 PM), http://www.theatlantic.com/national/archive/2012/06/from-off-the-wall-to-on-the-wall-how-the-mandate-challenge-went-mainstream/258040/ (Jack Balkin has described how certain arguments go from being ‘off the wall‘ to respectable in constitutional thought; economists have yet to take up that deflationary nomenclature for the evolution of ideas in their own field’s intellectual history. That helps explain the rising power of economists vis a vis lawyers, since the latter field’s honesty about the vagaries of its development diminishes its authority as a ‘science.’). For more on the political consequences of the philosophy of social science, see Jamie Cohen-Cole, The Open Mind: Cold War Politics and the Sciences of Human Nature (2014), and Joel Isaac, Working Knowledge: Making the Human Sciences from Parsons to Kuhn (2012).
[43] Chris Giles, Piketty Findings Undercut by Errors, Fin. Times (May 23, 2014, 7:00 PM), http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/2/e1f343ca-e281-11e3-89fd-00144feabdc0.html#axzz399nSmEKj; Thomas Piketty, Addendum: Response to FT, Thomas Piketty (May 28, 2014), http://piketty.pse.ens.fr/files/capital21c/en/Piketty2014TechnicalAppendixResponsetoFT.pdf; Felix Salmon, The Piketty Pessimist, Reuters (April 25, 2014), http://blogs.reuters.com/felix-salmon/2014/04/25/the-piketty-pessimist/.
[44] Neil Irwin, Everything You Need to know About Thomas Piketty vs. The Financial Times, N.Y. Times (May 30, 2014), http://www.nytimes.com/2014/05/31/upshot/everything-you-need-to-know-about-thomas-piketty-vs-the-financial-times.html
[45] Javier Blas, The Fragile Middle: Rising Inequality in Africa Weighs on New Consumers, Fin. Times (Apr. 18, 2014), http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/49812cde-c566-11e3-89a9-00144feabdc0.html#axzz399nSmEKj.
[46] Jane Owen, Duke of Grafton Uses R&B to Restore Euston Hall’s Pleasure Grounds, Fin. Times (Apr. 18, 2014, 2:03 PM), http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/2/b49f6dd8-c3bc-11e3-870b-00144feabdc0.html#slide0.
[47] Larry Elliott, Britain’s Five Richest Families Worth More Than Poorest 20%, Guardian, Mar. 16, 2014, http://www.theguardian.com/business/2014/mar/17/oxfam-report-scale-britain-growing-financial-inequality#101.
[48] Piketty, supra note 4, at 570.
[49] Margaret Kimberley, Freedom Rider: Miners Shot Down, Black Agenda Report (June 4, 2014), http://www.blackagendareport.com/content/freedom-rider-miners-shot-down.
[50] Peter Maass, Crude World: The Violent Twilight of Oil (2009); Nicholas Shaxson, Poisoned Wells: The Dirty Politics of African Oil (2008).
[51] Piketty, supra note 4, at 539.
[52] Jad Mouawad, Oil Corruption in Equatorial Guinea, N.Y. Times Green Blog (July 9, 2009, 7:01 AM), http://green.blogs.nytimes.com/2009/07/09/oil-corruption-in-equatorial-guinea; Tina Aridas & Valentina Pasquali, Countries with the Highest GDP Average Growth, 2003–2013, Global Fin. (Mar. 7, 2013), http://www.gfmag.com/component/content/article/119-economic-data/12368-countries-highest-gdp-growth.html#axzz2W8zLMznX; CIA, The World Factbook 184 (2007).
[53] Interview with President Teodoro Obiang of Equatorial Guinea, CNN’s Amanpour (CNN broadcast Oct. 5, 2012), transcript available at http://edition.cnn.com/TRANSCRIPTS/1210/05/ampr.01.html.
[54] Peter Maass, A Touch of Crude, Mother Jones, Jan. 2005,http://www.motherjones.com/politics/2005/01/obiang-equatorial-guinea-oil-riggs.
[55] Geraud Magrin & Geert van Vliet, The Use of Oil Revenues in Africa, in Governance of Oil in Africa: Unfinished Business 114 (Jacques Lesourne ed., 2009).
[56] Interview with President Teodoro Obiang of Equatorial Guinea, supra note 89 .
[57] S. Minority Staff of Permanent Subcomm. on Investigations, Comm. on Gov’t Affairs, 108th Cong., Rep. on Money Laundering and Foreign Corruption: Enforcement and Effectiveness of the Patriot Act 39-40 (Subcomm. Print 2004).
[58] Henry, supra note 68 , at 6, 19-20.
[59] Frank Pasquale, Closed Circuit Economics, New City Reader, Dec. 3, 2010, at 3, at http://neildonnelly.net/ncr/08_Business/NCR_Business_%5BF%5D_web.pdf.
[60] Liu Xiaobo, No Enemies, No Hatred 102 (Perry Link, trans., 2012).
[61] Jesse Drucker, Occupy Wall Street Stylists Pursue U.K. Tax Dodgers, Bloomberg News (June 11, 2013), http://www.businessweek.com/news/2013-06-11/occupy-wall-street-stylists-pursue-u-dot-k-dot-tax-dodgers.
[62] Daniel J. Mitchell, Tax Havens Should Be Emulated, Not Prosecuted, CATO Inst. (Apr. 13, 2009, 12:36 PM), http://www.cato.org/blog/tax-havens-should-be-emulated-not-prosecuted.
[63] Janet Novack, Pritzker Family Baggage: Tax Saving Offshore Trusts, Forbes (May 2, 2013, 8:20 PM), http://www.forbes.com/sites/janetnovack/2013/05/02/pritzker-family-baggage-tax-saving-offshore-trusts/.
[64] Ronen Palan et al., Tax Havens: How Globalization Really Works (2013); see also Carolyn Nordstrom, Global Outlaws: Crime, Money, and Power in the Contemporary World (2007), and Loretta Napoleoni, Rogue Economics (2009).
[65] Palan et al., supra note 100 .
[66] Shaxson, supra note 86 , at 24.
[67] Arianna Huffington, Third World America: How Our Politicians Are Abandoning the Middle Class and Betraying the American Dream (2011); Jeffrey A. Winters, Oligarchy (2011); Susan B. Crawford, Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age (2014).
[68] Benjamin Kunkel, Paupers and Richlings, 36 London Rev. Books 17 (2014) (reviewing Thomas Piketty, Capital in the Twenty-First Century).
[69] Jeffrey A. Winters, Oligarchy and Democracy, Am. Interest, Sept. 28, 2011, http://www.the-american-interest.com/articles/2011/9/28/oligarchy-and-democracy/.
[70] Id.
[71] James K. Galbraith, The Predator State: How Conservatives Abandoned the Free Market and Why Liberals Should, Too (2009).
[72] Alex Duval Smith, South Africa Lonmin Mine Massacre Puts Nationalism Back on Agenda, Guardian (Aug. 29, 2012), http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/poverty-matters/2012/aug/29/south-africa-lonmin-mine-massacre-nationalisation; Charlie Campbell, Dying for Some New Clothes: Bangladesh’s Rana Plaza Tragedy, Time (Apr. 26, 2013), http://world.time.com/2013/04/26/dying-for-some-new-clothes-the-tragedy-of-rana-plaza/; David Stuckler, The Body Economic: Why Austerity Kills xiv (2013); Soutik Biswas, India’s Micro-Finance Suicide Epidemic, BBC (Dec. 16, 2010), http://www.bbc.com/news/world-south-asia-11997571; Michael P. O’Donnell, Further Erosion of Our Moral Compass: Failure to Expand Medicaid to Low-Income People in All States, 28 Am. J. Health Promotion iv (2013); Sam Dickman et al., Opting Out of Medicaid Expansion; The Health and Financial Impacts, Health Affairs Blog (Jan. 30, 2014), http://healthaffairs.org/blog/2014/01/30/opting-out-of-medicaid-expansion-the-health-and-financial-impacts/.
[73] It would be instructive to compare political theorists’ varying models of Tocqueville’s predictive efforts, with Piketty’s sweeping r > g. See, e.g., Roger Boesche, Why Could Tocqueville Predict So Well?, 11 Political Theory 79 (1983) (“Democracy in America endeavors to demonstrate how language, literature, the relations of masters and servants, the status of women, the family, property, politics, and so forth, must change and align themselves in a new, symbiotic configuration as a result of the historical thrust toward equality”); Jon Elster, Alexis de Tocqueville: the First Social Scientist (2012).
[74] See, e.g., Frank Pasquale, Access to Medicine in an Era of Fractal Inequality, 19 Annals of Health Law 269 (2010); Frank Pasquale, The Cost of Conscience: Quantifying our Charitable Burden in an Era of Globalization, at http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=584741 (2004); Frank Pasquale, Diagnosing Finance’s Failures: From Economic Idealism to Lawyerly Realism, 6 India L. J. 2 (2012).
[75] Malcolm Harris interview of Alex Rivera, Border Control, New Inquiry (July 2, 2012), http://thenewinquiry.com/features/border-control/.
[76] Trebor Scholz, Digital Labor (Palgrave, forthcoming, 2015); Frank Pasquale, Banana Republic.com, Jotwell (Jan. 14, 2011), http://cyber.jotwell.com/banana-republic-com/.
[77] The Rise of Micro-Labor, On Point with Tom Ashbrook (NPR Apr. 3, 2012, 10:00 AM), http://onpoint.wbur.org/2012/04/03/micro-labor-websites.
[78] Vacation Time, On Point with Tom Ashbrook (NPR June 22, 2012, 10:00 AM), http://onpoint.wbur.org/2012/06/22/vacation-time.
[79] Peter Ryan, Aussies Must Compete with $2 a Day Workers: Rinehart, ABC News (Sept. 25, 2012, 2:56 PM), http://www.abc.net.au/news/2012-09-05/rinehart-says-aussie-workers-overpaid-unproductive/4243866.
[80] Roberto Patricio Korzeniewicz & Timothy Patrick Moran, Unveiling Inequality, at xv (2012).
[81] Ha Joon Chang, 23 Things They Don’t Tell You About Capitalism 98 (2012).
[82] Jason Burke, Over 40% of Indian Children Are Malnourished, Report Finds, Guardian (Jan. 10, 2012), http://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/jan/10/child-malnutrition-india-national-shame.
[83] Paul Farmer observes that “an understanding of poverty must be linked to efforts to end it.” Farmer, In the Company of the Poor, at http://www.pih.org/blog/in-the-company-of-the-poor. The same could be said of extreme inequality.
-

Nuruddin Farah joins the b2 Editorial Board
boundary 2 is proud and honored to announce that novelist Nuruddin Farah has joined the Editorial Board.
Below, he reads from his novels Maps and Crossbones at last year’s Fall 2013 conference: Legacies of the Future: The Life and Work of Edward Said.
-
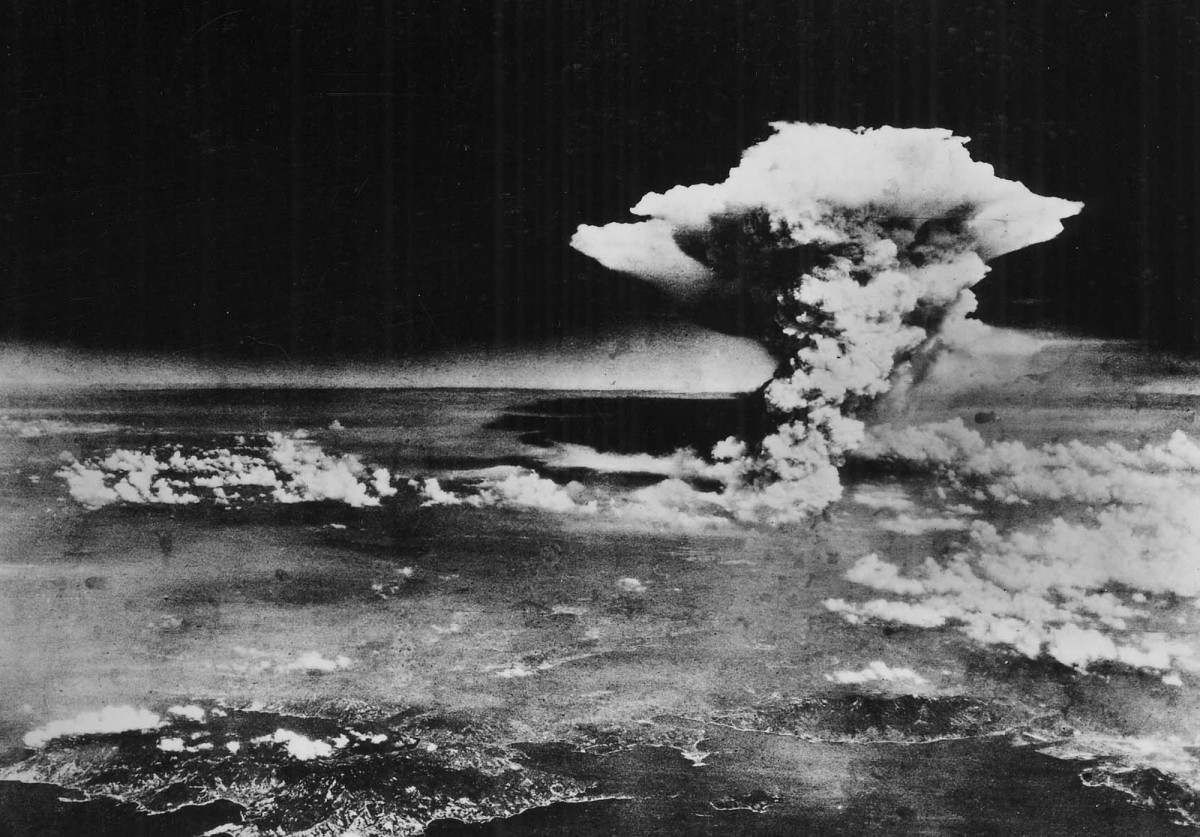

Henry A. Giroux — The Responsibility of Intellectuals in the Shadow of the Atomic Plague
Seventy years after the horror of Hiroshima, intellectuals negotiate a vastly changed cultural, political and moral geography. Pondering what Hiroshima means for American history and consciousness proves as fraught an intellectual exercise as taking up this critical issue in the years and the decades that followed this staggering inhumanity, albeit for vastly different reasons. Now that we are living in a 24/7 screen culture hawking incessant apocalypse, how we understand Foucault’s pregnant observation that history is always a history of the present takes on a greater significance, especially in light of the fact that historical memory is not simply being rewritten but is disappearing.1 Once an emancipatory pedagogical and political project predicated on the right to study, and engage the past critically, history has receded into a depoliticizing culture of consumerism, a wholesale attack on science, the glorification of military ideals, an embrace of the punishing state, and a nostalgic invocation of the greatest generation. Inscribed in insipid patriotic platitudes and decontextualized isolated facts, history under the reign of neoliberalism has been either cleansed of its most critical impulses and dangerous memories, or it has been reduced to a contrived narrative that sustains the fictions and ideologies of the rich and powerful. History has not only become a site of collective amnesia but has also been appropriated so as to transform “the past into a container full of colorful or colorless, appetizing or insipid bits, all floating with the same specific gravity.”2 Consequently, what intellectuals now have to say about Hiroshima and history in general is not of the slightest interest to nine tenths of the American population. While writers of fiction might find such a generalized, public indifference to their craft, freeing, even “inebriating” as Philip Roth has recently written, for the chroniclers of history it is a cry in the wilderness.3
At same time the legacy of Hiroshima is present but grasped, as the existential anxieties and dread of nuclear annihilation that racked the early 1950s to a contemporary fundamentalist fatalism embodied in collective uncertainty, a predilection for apocalyptic violence, a political economy of disposability, and an expanding culture of cruelty that has fused with the entertainment industry. We’ve not produced a generation of war protestors or government agitators to be sure, but rather a generation of youth who no longer believe they have a future that will be any different from the present.4 That such connections tying the past to the present are lost signal not merely the emergence of a disimagination machine that wages an assault on historical memory, civic literacy, and civic agency. It also points to a historical shift in which the perpetual disappearance of that atomic moment signals a further deepening in our own national psychosis.
If, as Edward Glover once observed, “Hiroshima and Nagasaki had rendered actual the most extreme fantasies of world destruction encountered in the insane or in the nightmares of ordinary people,” the neoliberal disimagination machine has rendered such horrific reality a collective fantasy driven by the spectacle of violence, nourished by sensationalism, and reinforced by scourge of commodified and trivialized entertainment.5 The disimagination machine threatens democratic public life by devaluing social agency, historical memory, and critical consciousness and in doing so it creates the conditions for people to be ethically compromised and politically infantilized. Returning to Hiroshima is not only necessary to break out of the moral cocoon that puts reason and memory to sleep but also to rediscover both our imaginative capacities for civic literacy on behalf of the public good, especially if such action demands that we remember as Robert Jay Lifton and Greg Mitchell remark “Every small act of violence, then, has some connection with, if not sanction from, the violence of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.”6
On Monday August 6, 1945 the United States unleashed an atomic bomb on Hiroshima killing 70,000 people instantly and another 70,000 within five years—an opening volley in a nuclear campaign visited on Nagasaki in the days that followed.7 In the immediate aftermath, the incineration of mostly innocent civilians was buried in official government pronouncements about the victory of the bombings of both Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The atomic bomb was celebrated by those who argued that its use was responsible for concluding the war with Japan. Also applauded was the power of the bomb and the wonder of science in creating it, especially “the atmosphere of technological fanaticism” in which scientists worked to create the most powerful weapon of destruction then known to the world.8 Conventional justification for dropping the atomic bombs held that “it was the most expedient measure to securing Japan’s surrender [and] that the bomb was used to shorten the agony of war and to save American lives.”9 Left out of that succinct legitimating narrative were the growing objections to the use of atomic weaponry put forth by a number of top military leaders and politicians, including General Dwight Eisenhower, who was then the Supreme Allied Commander in Europe, former President Herbert Hoover, and General Douglas MacArthur, all of whom argued it was not necessary to end the war.10 A position later proven to be correct.
For a brief time, the Atom Bomb was celebrated as a kind of magic talisman entwining salvation and scientific inventiveness and in doing so functioned to “simultaneously domesticate the unimaginable while charging the mundane surroundings of our everyday lives with a weight and sense of importance unmatched in modern times.”11 In spite of the initial celebration of the effects of the bomb and the orthodox defense that accompanied it, whatever positive value the bomb may have had among the American public, intellectuals, and popular media began to dissipate as more and more people became aware of the massive deaths along with suffering and misery it caused.12
Kenzaburo Oe, the Nobel Prize winner for Literature, noted that in spite of attempts to justify the bombing “from the instant the atomic bomb exploded, it [soon] became the symbol of human evil, [embodying] the absolute evil of war.”13 What particularly troubled Oe was the scientific and intellectual complicity in the creation of and in the lobbying for its use, with acute awareness that it would turn Hiroshima into a “vast ugly death chamber.”14 More pointedly, it revealed a new stage in the merging of military actions and scientific methods, indeed a new era in which the technology of destruction could destroy the earth in roughly the time it takes to boil an egg. The bombing of Hiroshima extended a new industrially enabled kind of violence and warfare in which the distinction between soldiers and civilians disappeared and the indiscriminate bombing of civilians was normalized. But more than this, the American government exhibited a ‘total embrace of the atom bomb,” that signalled support for the first time of a “notion of unbounded annihilation [and] “the totality of destruction.”15
Hiroshima designated the beginning of the nuclear era in which as Oh Jung points out “Combatants were engaged on a path toward total war in which technological advances, coupled with the increasing effectiveness of an air strategy, began to undermine the ethical view that civilians should not be targeted… This pattern of wholesale destruction blurred the distinction between military and civilian casualties.”16 The destructive power of the bomb and its use on civilians also marked a turning point in American self-identity in which the United States began to think of itself as a superpower, which as Robert Jay. Lifton points out refers to “a national mindset–put forward strongly by a tight-knit leadership group–that takes on a sense of omnipotence, of unique standing in the world that grants it the right to hold sway over all other nations.”17 The power of the scientific imagination and its murderous deployment gave birth simultaneously to the American disimagination machine with its capacity to rewrite history in order to render it an irrelevant relic best forgotten.
What remains particularly ghastly about the rationale for dropping two atomic bombs was the attempt on the part of its defenders to construct a redemptive narrative through a perversion of humanistic commitment, of mass slaughter justified in the name of saving lives and winning the war.18 This was a humanism under siege, transformed into its terrifying opposite and placed on the side of what Edmund Wilson called the Faustian possibility of a grotesque “plague and annihilation.”19 In part, Hiroshima represented the achieved transcendence of military metaphysics now a defining feature of national identity, its more poisonous and powerful investment in the cult of scientism, instrumental rationality, and technological fanaticism—and the simultaneous marginalization of scientific evidence and intellectual rigour, even reason itself. That Hiroshima was used to redefine America’s “national mission and its utopian possibilities”20 was nothing short of what the late historian Howard Zinn called a “devastating commentary on our moral culture.”21 More pointedly it serves as a grim commentary on our national sanity. In most of these cases, matters of morality and justice were dissolved into technical questions and reductive chauvinism relating matters of governmentally massaged efficiency, scientific “expertise”, and American exceptionalism. As Robert Jay Lifton and Greg Mitchell stated, the atom bomb was symbolic of the power of post-war America rather than a “ruthless weapon of indiscriminate destruction” which conveniently put to rest painful questions concerning justice, morality, and ethical responsibility. They write:
Our official narrative precluded anything suggesting atonement. Rather the bomb itself had to be “redeemed”: As “a frightening manifestation of technological evil … it needed to be reformed, transformed, managed, or turned into the vehicle of a promising future,” [as historian M. Susan] Lindee argued. “It was necessary, somehow, to redeem the bomb.” In other words, to avoid historical and moral responsibility, we acted immorally and claimed virtue. We sank deeper, that is, into moral inversion.22
This narrative of redemption was soon challenged by a number of historians who argued that the dropping of the atom bomb had less to do with winning the war than with an attempt to put pressure on the Soviet Union to not expand their empire into territory deemed essential to American interests.23 Protecting America’s superiority in a potential Soviet-American conflict was a decisive factor in dropping the bomb. In addition, the Truman administration needed to provide legitimation to Congress for the staggering sums of money spent on the Manhattan Project in developing the atomic weapons program and for procuring future funding necessary to continue military appropriations for ongoing research long after the war ended.24 Howard Zinn goes even further asserting that the government’s weak defense for the bombing of Hiroshima was not only false but was complicitous with an act of terrorism. Refusing to relinquish his role as a public intellectual willing to hold power accountable, he writes “Can we … comprehend the killing of 200,000 people to make a point about American power?”25 A number of historians, including Gar Alperowitz and Tsuyoshi Hasegawa, also attempted to deflate this official defense of Hiroshima by providing counter-evidence that the Japanese were ready to surrender as a result of a number of factors including the nonstop bombing of 26 cities before Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the success of the naval and military blockade of Japan, and the Soviet’s entrance into the war on August 9th.26
The narrative of redemption and the criticism it provoked are important for understanding the role that intellectuals assumed at this historical moment to address what would be the beginning of the nuclear weapons era and how that role for critics of the nuclear arms race has faded somewhat at the beginning of the twenty-first century. Historical reflection on this tragic foray into the nuclear age reveals the decades long dismantling of a culture’s infrastructure of ideas, its growing intolerance for critical thought in light of the pressures placed on media, on universities and increasingly isolated intellectuals to support comforting mythologies and official narratives and thus cede the responsibility to give effective voice to unpopular realities.
Within a short time after the dropping of the atom bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, John Hersey wrote a devastating description of the misery and suffering caused by the bomb. Removing the bomb from abstract arguments endorsing matters of technique, efficiency, and national honor, Hersey first published in The New Yorker and later in a widely read book an exhausting and terrifying description of the bombs effects on the people of Hiroshima, portraying in detail the horror of the suffering caused by the bomb. There is one haunting passage that not only illustrates the horror of the pain and suffering, but also offers a powerful metaphor for the blindness that overtook both the victims and the perpetrators. He writes:
On his way back with the water, [Father Kleinsorge] got lost on a detour around a fallen tree, and as he looked for his way through the woods, he heard a voice ask from the underbrush, ‘Have you anything to drink?’ He saw a uniform. Thinking there was just one soldier, he approached with the water. When he had penetrated the bushes, he saw there were about twenty men, they were all in exactly the same nightmarish state: their faces were wholly burned, their eye sockets were hollow, the fluid from their melted eyes had run down their cheeks. Their mouths were mere swollen, pus-covered wounds, which they could not bear to stretch enough to admit the spout of the teapot.27
The nightmarish image of fallen soldiers staring with hollow sockets, eyes liquidated on cheeks and mouths swollen and pus-filled stands as a warning to those who would refuse blindly the moral witnessing necessary to keep alive for future generations the memory of the horror of nuclear weapons and the need to eliminate them. Hersey’s literal depiction of mass violence against civilians serves as a kind of mirrored doubling, referring at one level to nations blindly driven by militarism and hyper-nationalism. At another level, perpetrators become victims who soon mimic their perpetrators, seizing upon their own victimization as a rationale to become blind to their own injustices.
Pearl Harbor enabled Americans to view themselves as the victims but then assumed the identity of the perpetrators and became willfully blind to the United States’ own escalation of violence and injustice. Employing both a poisonous racism and a weapon of mad violence against the Japanese people, the US government imagined Japan as the ultimate enemy, and then pursued tactics that blinded the American public to its own humanity and in doing so became its own worst enemy by turning against its most cherished democratic principles. In a sense, this self-imposed sightlessness functioned as part of what Jacques Derrida once called a societal autoimmune response, one in which the body’s immune system attacked its own bodily defenses.28 Fortunately, this state of political and moral blindness did not extend to a number of critics for the next fifty years who railed aggressively against the dropping of the atomic bombs and the beginning of the nuclear age.
Responding to Hersey’s article on the bombing of Hiroshima published in The New Yorker, Mary McCarthy argued that he had reduced the bombing to the same level of journalism used to report natural catastrophes such as “fires, floods, and earthquakes” and in doing so had reduced a grotesque act of barbarism to “a human interest story” that had failed to grasp the bomb’s nihilism, and the role that “bombers, the scientists, the government” and others played in producing this monstrous act.29 McCarthy was alarmed that Hersey had “failed to consider why it was used, who was responsible, and whether it had been necessary.”30 McCarthy was only partly right. While it was true that Hersey didn’t tackle the larger political, cultural and social conditions of the event’s unfolding, his article provided one of the few detailed reports at the time of the horrors the bomb inflicted, stoking a sense of trepidation about nuclear weapons along with a modicum of moral outrage over the decision to drop the bomb—dispositions that most Americans had not considered at the time. Hersey was not alone. Wilfred Burchett, writing for the London Daily Express, was the first journalist to provide an independent account of the suffering, misery, and death that engulfed Hiroshima after the bomb was dropped on the city. For Burchett, the cataclysm and horror he witnessed first-hand resembled a vision of hell that he aptly termed “the Atomic Plague.” He writes:
Hiroshima does not look like a bombed city. It looks as if a monster steamroller had passed over it and squashed it out of existence. I write these facts as dispassionately as I can in the hope that they will act as a warning to the world. In this first testing ground of the atomic bomb I have seen the most terrible and frightening desolation in four years of war. It makes a blitzed Pacific island seem like an Eden. The damage is far greater than photographs can show.31
In the end in spite of such accounts, fear and moral outrage did little to put an end to the nuclear arms race, but it did prompt a number of intellectuals to enter into the public realm to denounce the bombing and the ongoing advance of a nuclear weapons program and the ever-present threat of annihilation it posed. In the end, fear and moral outrage did little to put an end to the nuclear arms race, but it did prompt a number of intellectuals to enter into the public realm to denounce the bombing and the ongoing advance of a nuclear weapons program and the ever-present threat of annihilation it posed.
A number of important questions emerge from the above analysis, but two issues in particular stand out for me in light of the role that academics and public intellectuals have played in addressing the bombing of Hiroshima and the emergence of a nuclear weapons on a global scale, and the imminent threat of human annihilation posed by the continuing existence and danger posed by the potential use of such weapons. The first question focuses on what has been learned from the bombing of Hiroshima and the second question concerns the disturbing issue of how violence and hence Hiroshima itself have become normalized in the collective American psyche.
In the aftermath of the bombing of Hiroshima, there was a major debate not just about how the emergence of the atomic age and the moral, economic, scientific, military, and political forced that gave rise to it. There was also a heated debate about the ways in which the embrace of the atomic age altered the emerging nature of state power, gave rise to new forms of militarism, put American lives at risk, created environmental hazards, produced an emergent surveillance state, furthered the politics of state secrecy, and put into play a series of deadly diplomatic crisis, reinforced by the logic of brinkmanship and a belief in the totality of war.32
Hiroshima not only unleashed immense misery, unimaginable suffering, and wanton death on Japanese civilians, it also gave rise to anti-democratic tendencies in the United States government that put the health, safety, and liberty of the American people at risk. Shrouded in secrecy, the government machinery of death that produced the bomb did everything possible to cover up the most grotesque effects of the bomb on the people of Hiroshima and Nagasaki but also the dangerous hazards it posed to the American people. Lifton and Mitchell argue convincingly that if the development of the bomb and its immediate effects were shrouded in concealment by the government that before long concealment developed into a cover up marked by government lies and the falsification of information.33 With respect to the horrors visited upon Hiroshima and Nagasaki, films taken by Japanese and American photographers were hidden for years from the American public for fear that they would create both a moral panic and a backlash against the funding for nuclear weapons.34 For example, the Atomic Energy Commission lied about the extent and danger of radiation fallout going so far as to mount a campaign claiming that “fallout does not constitute a serious hazard to any living thing outside the test site.”35 This act of falsification took place in spite of the fact that thousands of military personal were exposed to high levels of radiation within and outside of the test sites.
In addition, the Atomic Energy Commission in conjunction with the Departments of Defense, Department of Veterans’ Affairs, the Central Intelligence Agency, and other government departments engaged in a series of medical experiments designed to test the effects of different levels radiation exposure on military personal, medical patients, prisoners, and others in various sites. According to Lifton and Mitchell, these experiments took the shape of exposing people intentionally to “radiation releases or by placing military personnel at or near ground zero of bomb tests.”36 It gets worse. They also note that “from 1945 through 1947, bomb-grade plutonium injections were given to thirty-one patients [in a variety of hospitals and medical centers] and that all of these “experiments were shrouded in secrecy and, when deemed necessary, in lies….the experiments were intended to show what type or amount of exposure would cause damage to normal, healthy people in a nuclear war.”37 Some of the long lasting legacies of the birth of the atomic bomb also included the rise of plutonium dumps, environmental and health risks, the cult of expertise, and the subordination of the peaceful development technology to a large scale interest in using technology for the organized production of violence. Another notable development raised by many critics in the years following the launch of the atomic age was the rise of a government mired in secrecy, the repression of dissent, and the legitimation for a type of civic illiteracy in which Americans were told to leave “the gravest problems, military and social, completely in the hands of experts and political leaders who claimed to have them under control.”38
All of these anti-democratic tendencies unleashed by the atomic age came under scrutiny during the latter half of the twentieth century. The terror of a nuclear holocaust, an intense sense of alienation from the commanding institutions of power, and deep anxiety about the demise of the future spawned growing unrest, ideological dissent, and massive outbursts of resistance among students and intellectuals all over the globe from the sixties until the beginning of the twenty-first century calling for the outlawing of militarism, nuclear production and stockpiling, and the nuclear propaganda machine. Literary writers extending from James Agee to Kurt Vonnegut, Jr. condemned the death-saturated machinery launched by the atomic age. Moreover, public intellectuals from Dwight Macdonald and Bertrand Russell to Helen Caldicott, Ronald Takaki, Noam Chomsky, and Howard Zinn, fanned the flames of resistance to both the nuclear arms race and weapons as well as the development of nuclear technologies. Others such as George Monbiot, an environmental activist, have supported the nuclear industry but denounced the nuclear arms race. In doing so, he has argued that “The anti-nuclear movement … has misled the world about the impacts of radiation on human health [producing] claims … ungrounded in science, unsupportable when challenged and wildly wrong [and] have done other people, and ourselves, a terrible disservice.”39
In addition, in light of the nuclear crises that extend from the Three Mile accident in 1979, the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 and the more recent Fukushima nuclear disaster in 2011, a myriad of social movements along with a number of mass demonstrations against nuclear power have developed and taken place all over the world.40 While deep moral and political concerns over the legacy of Hiroshima seemed to be fading in the United States, the tragedy of 9/11 and the endlessly replayed images of the two planes crashing into the twin towers of the World Trade Center resurrected once again the frightening image of what Colonel Paul Tibbetts, Jr., the Enola Gay’s pilot, referred to as “that awful cloud… boiling up, mushrooming, terrible and incredibly tall” after “Little Boy,” a 700-pound uranium bomb was released over Hiroshima. Though this time, collective anxieties were focused not on the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and its implications for a nuclear Armageddon but on the fear of terrorists using a nuclear weapon to wreak havoc on Americans. But a decade later even that fear, however parochially framed, seems to have been diminished if not entirely, erased even though it has produced an aggressive attack on civil liberties and given even more power to an egregious and dangerous surveillance state.
Atomic anxiety confronts a world in which 9 states have nuclear weapons and a number of them such as North Korea, Pakistan, and India have threatened to use them. James McCluskey points out that “there are over 20,0000 nuclear weapons in existence, sufficient destructive power to incinerate every human being on the planet three times over [and] there are more than 2000 held on hair trigger alert, already mounted on board their missiles and ready to be launched at a moment’s notice.”41 These weapons are far more powerful and deadly than the atomic bomb and the possibility that they might be used, even inadvertently, is high. This threat becomes all the more real in light of the fact that the world has seen a history of miscommunications and technological malfunctions, suggesting both the fragility of such weapons and the dire stupidity of positions defending their safety and value as a nuclear deterrent.42 The 2014 report, To Close for Comfort—Cases of Near Nuclear Use and Options for Policy not only outlines a history of such near misses in great detail, it also makes terrifyingly clear that “the risk associated with nuclear weapons is high.”43 It is also worth noting that an enormous amount of money is wasted to maintain these weapons and missiles, develop more sophisticated nuclear weaponries, and invest in ever more weapons laboratories. McCluskey estimates world funding for such weapons at $1trillion per decade while Arms Control Today reported in 2012 that yearly funding for U.S. nuclear weapons activity was $31 billion.44
In the United States, the mushroom cloud connected to Hiroshima is now connected to much larger forces of destruction, including a turn to instrumental reason over moral considerations, the normalization of violence in America, the militarization of local police forces, an attack on civil liberties, the rise of the surveillance state, a dangerous turn towards state secrecy under President Obama, the rise of the carceral state, and the elevation of war as a central organizing principle of society. Rather than stand in opposition to preventing a nuclear mishap or the expansion of the arms industry, the United States places high up on the list of those nations that could trigger what Amy Goodman calls that “horrible moment when hubris, accident or inhumanity triggers the next nuclear attack.”45 Given the history of lies, deceptions, falsifications, and retreat into secrecy that characterizes the American government’s strangulating hold by the military-industrial-surveillance complex, it would be naïve to assume that the U.S. government can be trusted to act with good intentions when it comes to matters of domestic and foreign policy. State terrorism has increasingly become the DNA of American governance and politics and is evident in government cover ups, corruption, and numerous acts of bad faith. Secrecy, lies, and deception have a long history in the United States and the issue is not merely to uncover such instances of state deception but to connect the dots over time and to map the connections, for instance, between the actions of the NSA in the early aftermath of the attempts to cover up the inhumane destruction unleashed by the atomic bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki and the role the NSA and other intelligence agencies play today in distorting the truth about government policies while embracing an all-compassing notion of surveillance and squelching of civil liberties, privacy, and freedom.
Hiroshima symbolizes the fact that the United States commits unspeakable acts making it easier to refuse to rely on politicians, academics, and alleged experts who refuse to support a politics of transparency and serve mostly to legitimate anti-democratic, if not totalitarian policies. Questioning a monstrous war machine whose roots lie in Hiroshima is the first step in declaring nuclear weapons unacceptable ethically and politically. This suggests a further mode of inquiry that focuses on how the rise of the military-industrial complex contributes to the escalation of nuclear weapons and what can we learn by tracing it roots to the development and use of the atom bomb. Moreover, it raises questions about the role played by intellectuals both in an out of the academy in conspiring to build the bomb and hide its effects from the American people? These are only some of the questions that need to be made visible, interrogated, and pursued in a variety of sites and public forums.
One crucial issue today is what role might intellectuals and matters of civic courage, engaged citizenship, and the educative nature of politics play as part of a sustained effort to resurrect the memory of Hiroshima as both a warning and a signpost for rethinking the nature of collective struggle, reclaiming the radical imagination, and producing a sustained politics aimed at abolishing nuclear weapons forever? One issue would be to revisit the conditions that made Hiroshima and Nagasaki possible, to explore how militarism and a kind of technological fanaticism merged under the star of scientific rationality. Another step forward would be to make clear what the effects of such weapons are, to disclose the manufactured lie that such weapons make us safe. Indeed, this suggests the need for intellectuals, artists, and other cultural workers to use their skills, resources, and connections to develop massive educational campaigns.
Such campaigns not only make education, consciousness, and collective struggle the center of politics, but also systemically work to both inform the public about the history of such weapons, the misery and suffering they have caused, and how they benefit the financial, government, and corporate elite who make huge amounts of money off the arms race and the promotion of nuclear deterrence and the need for a permanent warfare state. Intellectuals today appear numbed by ever developing disasters, statistics of suffering and death, the Hollywood disimagination machine with its investment in the celluloid Apocalypse for which only superheroes can respond, and a consumer culture that thrives on self-interests and deplores collective political and ethical responsibility.
There are no rationales or escapes from the responsibility of preventing mass destruction due to nuclear annihilation; the appeal to military necessity is no excuse for the indiscriminate bombing of civilians whether in Hiroshima or Afghanistan. The sense of horror, fear, doubt, anxiety, and powerless that followed Hiroshima and Nagasaki up until the beginning of the 21st century seems to have faded in light of both the Hollywood apocalypse machine, the mindlessness of celebrity and consumer cultures, the growing spectacles of violence, and a militarism that is now celebrated as one of the highest ideals of American life. In a society governed by militarism, consumerism, and neoliberal savagery, it has become more difficult to assume a position of moral, social, and political responsibility, to believe that politics matters, to imagine a future in which responding to the suffering of others is a central element of democratic life. When historical memory fades and people turn inward, remove themselves from politics, and embrace cynicism over educated hope, a culture of evil, suffering, and existential despair. Americans now life amid a culture of indifference sustained by an endless series of manufactured catastrophes that offer a source of entertainment, sensation, and instant pleasure.
We live in a neoliberal culture that subordinates human needs to the demand for unchecked profits, trumps exchange values over the public good, and embraces commerce as the only viable model of social relations to shape the entirety of social life. Under such circumstances, violence becomes a form of entertainment rather than a source of alarm, individuals no longer question society and become incapable of translating private troubles into larger public considerations. In the age following the use of the atom bomb on civilians, talk about evil, militarism, and the end of the world once stirred public debate and diverse resistance movements, now it promotes a culture of fear, moral panics, and a retreat into the black hole of the disimagination machine. The good news is that neoliberalism now makes clear that it cannot provide a vision to sustain society and works largely to destroy it. It is a metaphor for the atom bomb, a social, political, and moral embodiment of global destruction that needs to be stopped before it is too late. The future will look much brighter without the glow of atomic energy and the recognition that the legacy of death and destruction that extends from Hiroshima to Fukushima makes clear that no one can be a bystander if democracy is to survive.
notes:
1. This reference refers to a collection of interviews with Michel Foucault originally published by Semiotext(e). Michel Foucault, “What our present is?” Foucault Live: Collected Interviews, 1961–1984, ed. Sylvere Lotringer, trans. Lysa Hochroth and John Johnston,(New York: Semiotext(e), 1989 and 1996), 407–415.
Back to the essay2. Zygmunt Bauman and Leonidas Donskis, Moral Blindness: The loss of Sensitivity in Liquid Modernity, (Cambridge, UK: Polity Press, 2013), p. 33.
Back to the essay3. Daniel Sandstrom Interviews Philip Roth, “My Life as a Writer,” New York Times (March 2, 2014). Online: http://www.nytimes.com/2014/03/16/books/review/my-life-as-a-writer.html
Back to the essay4. Of course, the Occupy Movement in the United States and the Quebec student movement are exceptions to this trend. See, for instance, David Graeber, The Democracy Project: A History, A Crisis, A Movement, (New York, NY,: The Random House Publishing Group, 2013) and Henry A. Giroux, Neoliberalism’s War Against Higher Education (Chicago: Haymarket, 2014).
Back to the essay5. Of course, the Occupy Movement in the United States and the Quebec student movement are exceptions to this trend. See, for instance, David Graeber, The Democracy Project: A History, A Crisis, A Movement, (New York, NY,: The Random House Publishing Group, 2013) and Henry A. Giroux, Neoliberalism’s War Against Higher Education (Chicago: Haymarket, 2014).
Back to the essay6. Ibid., Lifton and Mitchell, p. 345.
Back to the essay7. Jennifer Rosenberg, “Hiroshima and Nagasaki (Part 2),” About.com –20th Century History (March 28, 201). Online: http://history1900s.about.com/od/worldwarii/a/hiroshima_2.htm. A more powerful atom bomb was dropped on Nagasaki on August 9, 1945 and by the end of the year an estimated 70,000 had been killed. For the history of the making of the bomb, see the monumental: Richard Rhodes, The Making of the Atomic Bomb, Anv Rep edition (New York: Simon & Schuster, 2012.
Back to the essay8. The term “technological fanaticism” comes from Michael Sherry who suggested that it produced an increased form of brutality. Cited in Howard Zinn, The Bomb. (New York. N.Y.: City Lights, 2010), pp. 54-55.
Back to the essay9. Oh Jung, “Hiroshima and Nagasaki: The Decision to Drop the Bomb,” Michigan Journal of History Vol 1. No. 2 (Winter 2002). Online:
http://michiganjournalhistory.files.wordpress.com/2014/02/oh_jung.pdf.
Back to the essay10. See, in particular, Ronald Takaki, Hiroshima: Why America Dropped the Atomic Bomb, (Boston: Back Bay Books, 1996). http://michiganjournalhistory.files.wordpress.com/2014/02/oh_jung.pdf.
Back to the essay11. Peter Bacon Hales, Outside the Gates of Eden: The Dream Of America From Hiroshima To Now. (Chicago. IL.: University of Chicago Press, 2014), p. 17.
Back to the essay12. Paul Ham, Hiroshima Nagasaki: The Real Story of the Atomic Bombings and Their Aftermath (New York: Doubleday, 2011).
Back to the essay13. Kensaburo Oe, Hiroshima Notes (New York: Grove Press, 1965), p. 114.
Back to the essay14. Ibid., Oe, Hiroshima Notes, p. 117.
Back to the essay15. Robert Jay Lifton and Greg Mitchell, Hiroshima in America, (New York, N.Y.: Avon Books, 1995). p. 314-315. 328.
Back to the essay16. Ibid., Oh Jung, “Hiroshima and Nagasaki: The Decision to Drop the Bomb.”
Back to the essay17. Robert Jay Lifton, “American Apocalypse,” The Nation (December 22, 2003), p. 12.
Back to the essay18. For an interesting analysis of how the bomb was defended by the New York Times and a number of high ranking politicians, especially after John Hersey’s Hiroshima appeared in The New Yorker, see Steve Rothman, “The Publication of “Hiroshima” in The New Yorker,” Herseyheroshima.com, (January 8, 1997). Online: http://www.herseyhiroshima.com/hiro.php
Back to the essay19. Wilson cited in Lifton and Mitchell, Hiroshima In America, p. 309.
Back to the essay20. Ibid., Peter Bacon Hales, Outside The Gates of Eden: The Dream Of America From Hiroshima To Now, p. 8.
Back to the essay21. Ibid., Zinn, The Bomb, p. 26.
Back to the essay22. Ibid., Robert Jay Lifton and Greg Mitchell, Hiroshima In America.
Back to the essay23. For a more recent articulation of this argument, see Ward Wilson, Five Myths About Nuclear Weapons (new York: Mariner Books, 2013).
Back to the essay24. Ronald Takaki, Hiroshima: Why America Dropped the Atomic Bomb, (Boston: Back Bay Books, 1996), p. 39
Back to the essay25. Ibid, Zinn, The Bomb, p. 45.
Back to the essay26. See, for example, Ibid., Haseqawa; Gar Alperowitz’s, Atomic Diplomacy Hiroshima and Potsdam: The Use of the Atomic Bomb and the American Confrontation with Soviet Power (London: Pluto Press, 1994) and also Gar Alperowitz, The Decision to Use the Atomic Bomb (New York: Vintage, 1996). Ibid., Ham.
Back to the essay27. John Hersey, Hiroshima (New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1946), p. 68.
Back to the essay28. Giovanna Borradori, ed, “Autoimmunity: Real and Symbolic Suicides–a dialogue with Jacques Derrida,” in Philosophy in a Time of Terror: Dialogues with Jurgen Habermas and Jacques Derrida (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2004), pp. 85-136.
Back to the essay29. Mary McCarthy, “The Hiroshima “New Yorker”,” The New Yorker (November, 1946).
http://americainclass.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/mccarthy_onhiroshima.pdf
Back to the essay30. Ibid., Ham, Hiroshima Nagasaki, p. 469.
Back to the essay31. George Burchett & Nick Shimmin, eds. Memoirs of a Rebel Journalist: The Autobiography of Wilfred Burchett, (UNSW Press, Sydney, 2005), p.229.
Back to the essay32. For an informative analysis of the deep state and a politics driven by corporate power, see Bill Blunden, “The Zero-Sum Game of Perpetual War,” Counterpunch (September 2, 2014). Online: http://www.counterpunch.org/2014/09/02/the-zero-sum-game-of-perpetual-war/
Back to the essay33. The following section relies on the work of both Lifton and Mitchell, Howard Zinn, and M. Susan Lindee.
Back to the essay34. Greg Mitchell, “The Great Hiroshima Cover-up,” The Nation, (August 3, 2011). Online:
http://www.thenation.com/blog/162543/great-hiroshima-cover#. Also see, Greg Mitchell, “Part 1: Atomic Devastation Hidden For Decades,” WhoWhatWhy (March 26, 2014). Online: http://whowhatwhy.com/2014/03/26/atomic-devastation-hidden-decades; Greg Mitchell, “Part 2: How They Hid the Worst Horrors of Hiroshima,” WhoWhatWhy, (March 28, 2014). Online:
http://whowhatwhy.com/2014/03/28/part-2-how-they-hid-the-worst-horrors-of-hiroshima/; Greg Mitchell, “Part 3: Death and Suffering, in Living Color,” WhoWhatWhy (March 31, 2014). Online: http://whowhatwhy.com/2014/03/31/death-suffering-living-color/
Back to the essay35. Ibid., Robert Jay Lifton and Greg Mitchell, Hiroshima In America, p. 321.
Back to the essay36. Ibid., Robert Jay Lifton and Greg Mitchell, Hiroshima In America, p. 322.
Back to the essay37. Ibid. Robert Jay Lifton and Greg Mitchell, Hiroshima In America, p. 322-323.
Back to the essay38. Ibid. Robert Jay Lifton and Greg Mitchell, Hiroshima In America, p. 336.
Back to the essay39. George Monbiot, “Evidence Meltdown,” The Guardian (April 5, 2011). Online: http://www.monbiot.com/2011/04/04/evidence-meltdown/
Back to the essay40. Patrick Allitt, A Climate of Crisis: America in the Age of Environmentalism (New York: Penguin, 2015); Horace Herring, From Energy Dreams to Nuclear Nightmares: Lessons from the Anti-nuclear Power Movement in the 1970s (Chipping Norton, UK: Jon Carpenter Publishing, 2006; Alain Touraine, Anti-Nuclear Protest: The Opposition to Nuclear Energy in France (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1983); Stephen Croall, The Anti-Nuclear Handbook New York: Random House, 1979). On the decade that enveloped the anti-nuclear moment with a series of crisis, see Philip Jenkins, Decade of Nightmares: The End of the Sixties and the Making of Eighties America (New York: Oxford University Press, 2008).
Back to the essay41. James McCluskey, “Nuclear Crisis: Can the Sane Prevail in Time?” Truthout (June 10, 2014). Online: http://www.truth-out.org/opinion/item/24273
Back to the essay42. See, for example, the list of crisis, near misses, and nuclear war mongering that characterizes United States foreign policy in the last few decades, see, Noam Chomsky, “How Many Minutes to Midnight? Hiroshima Day 2014.” Truthout (August 5, 2014). Online: http://www.truth-out.org/news/item/25388-how-many-minutes-to-midnight-hiroshima-day-2014
Back to the essay43. Patricia Lewis, Heather Williams, Benoît Pelopidas and Sasan Aghlani, To Close for Comfort —Cases of Near Nuclear Use and Options for Policy (London: Chatham House, 2014). Online: http://www.chathamhouse.org/sites/files/chathamhouse/home/chatham/public_html/sites/default/files/20140428TooCloseforComfortNuclearUseLewisWilliamsPelopidasAghlani.pdf
Back to the essay44. Jim McCluskey, “Nuclear Deterrence: The Lie to End All Lies,” Truthout (Oct 29, 2012). Online: http://www.truth-out.org/opinion/item/12381
Back to the essay45. Amy Goodman, “Hiroshima and Nagasaki, 69 Year Later,” TruthDig (August 6, 2014). Online: http://www.truthdig.com/report/item/hiroshima_and_nagasaki_69_years_later_20140806
Back to the essay -

Democracy: An Unfinished Project

by Susan Buck-Morss
~This essay criticizes Ahmet Davutoğlu’s proposal that Islamic civilization complete the “unfinished project of modernity” (Jürgen Habermas), by challenging the concept of civilization itself. As scholars in multiple disciplines have demonstrated, civilizations are hybrid constructions that cannot be contained within a uniform conceptual frame, such as Islamic “authenticity.” The past is shared, and the present is as well. The Arab Spring demonstrates that modernity confronts political actors with similar problems, whatever their background. The essay addresses successive paradoxes within the unfinished project of democracy: the contradiction between free markets (capitalist inequality) and free societies (political equality), the hierarchical relationship between the people and their leaders (Jacques Ranciére’s Ignorant Schoolmaster is discussed), and the lack of democracy between nations within the present world order.
Read the full essay here.Summer 2014Feature Image: leaflet dropped on MNLA during the Malayan Emergency, offering $1,000 in exchange for the individual surrender of targeted MCP insurgents and the turning in of their Bren gun. A labeled “emergency” and not “war” for insurance purposes, it is suggested.