by Alexander R. Galloway and Andrew Culp
~
Alexander R. Galloway: You have a new book called Dark Deleuze (University of Minnesota Press, 2016). I particularly like the expression “canon of joy” that guides your investigation. Can you explain what canon of joy means and why it makes sense to use it when talking about Deleuze?
Andrew Culp: My opening is cribbed from a letter Gilles Deleuze wrote to philosopher and literary critic Arnaud Villani in the early 1980s. Deleuze suggests that any worthwhile book must have three things: a polemic against an error, a recovery of something forgotten, and an innovation. Proceeding along those three lines, I first argue against those who worship Deleuze as the patron saint of affirmation, second I rehabilitate the negative that already saturates his work, and third I propose something he himself was not capable of proposing, a “hatred for this world.” So in an odd twist of Marx on history, I begin with those who hold up Deleuze as an eternal optimist, yet not to stand on their shoulders but to topple the church of affirmation.
The canon portion of “canon of joy” is not unimportant. Perhaps more than any other recent thinker, Deleuze queered philosophy’s line of succession. A large portion of his books were commentaries on outcast thinkers that he brought back from exile. Deleuze was unwilling to discard Nietzsche as a fascist, Bergson as a spiritualist, or Spinoza as a rationalist. Apparently this led to lots of teasing by fellow agrégation students at the Sorbonne in the late ’40s. Further showing his strange journey through the history of philosophy, his only published monograph for nearly a decade was an anti-transcendental reading of Hume at a time in France when phenomenology reigned. Such an itinerant path made it easy to take Deleuze at his word as a self-professed practitioner of “minor philosophy.” Yet look at Deleuze’s outcasts now! His initiation into the pantheon even bought admission for relatively forgotten figures such as sociologist Gabriel Tarde. Deleuze’s popularity thus raises a thorny question for us today: how do we continue the minor Deleuzian line when Deleuze has become a “major thinker”? For me, the first step is to separate Deleuze (and Guattari) from his commentators.
I see two popular joyous interpretations of Deleuze in the canon: unreconstructed Deleuzians committed to liberating flows, and realists committed to belief in this world. The first position repeats the language of molecular revolution, becoming, schizos, transversality, and the like. Some even use the terms without transforming them! The resulting monotony seals Deleuze and Guattari’s fate as a wooden tongue used by people still living in the ’80s. Such calcification of their concepts is an especially grave injustice because Deleuze quite consciously shifted terminology from book to book to avoid this very outcome. Don’t get me wrong, I am deeply indebted to the early work on Deleuze! I take my insistence on the Marxo-Freudian core of Deleuze and Guattari from one of their earliest Anglophone commentators, Eugene Holland, who I sought out to direct my dissertation. But for me, the Tiqqun line “the revolution was molecular, and so was the counter-revolution” perfectly depicts the problem of advocating molecular politics. Why? Today’s techniques of control are now molecular. The result is that control societies have emptied the molecular thinker’s only bag of tricks (Bifo is a good test case here), which leaves us with a revolution that only goes one direction: backward.
I am equally dissatisfied by realist Deleuzians who delve deep into the early strata of A Thousand Plateaus and away from the “infinite speed of thought” that motivates What is Philosophy? I’m thinking of the early incorporations of dynamical systems theory, the ’90s astonishment over everything serendipitously looking like a rhizome, the mid-00s emergence of Speculative Realism, and the ongoing “ontological” turn. Anyone who has read Manuel DeLanda will know this exact dilemma of materiality versus thought. He uses examples that slow down Deleuze and Guattari’s concepts to something easily graspable. In his first book, he narrates history as a “robot historian,” and in A Thousand Years of Nonlinear History, he literally traces the last thousand years of economics, biology, and language back to clearly identifiable technological inventions. Such accounts are dangerously compelling due to their lucidity, but they come at a steep cost: android realism dispenses with Deleuze and Guattari’s desiring subject, which is necessary for a theory of revolution by way of the psychoanalytic insistence on the human ability to overcome biological instincts (e.g. Freud’s Instincts and their Vicissitudes and Beyond the Pleasure Principle). Realist interpretations of Deleuze conceive of the subject as fully of this world. And with it, thought all but evaporates under the weight of this world. Deleuze’s Hume book is an early version of this criticism, but the realists have not taken heed. Whether emergent, entangled, or actant, strong realists ignore Deleuze and Guattari’s point in What is Philosophy? that thought always comes from the outside at a moment when we are confronted by something so intolerable that the only thing remaining is to think.
Galloway: The left has always been ambivalent about media and technology, sometimes decrying its corrosive influence (Frankfurt School), sometimes embracing its revolutionary potential (hippy cyberculture). Still, you ditch technical “acceleration” in favor of “escape.” Can you expand your position on media and technology, by way of Deleuze’s notion of the machinic?
Culp: Foucault says that an episteme can be grasped as we are leaving it. Maybe we can finally catalogue all of the contemporary positions on technology? The romantic (computer will never capture my soul), the paranoiac (there is an unknown force pulling the strings), the fascist-pessimist (computers will control everything)…
Deleuze and Guattari are certainly not allergic to technology. My favorite quote actually comes from the Foucault book in which Deleuze says that “technology is social before it is technical” (6). The lesson we can draw from this is that every social formation draws out different capacities from any given technology. An easy example is from the nomads Deleuze loved so much. Anarcho-primitivists speculate that humans learn oppression with the domestication of animals and settled agriculture during the Neolithic Revolution. Diverging from the narrative, Deleuze celebrates the horse people of the Eurasian steppe described by Arnold Toynbee. Threatened by forces that would require them to change their habitat, Toynbee says, they instead chose to change their habits. The subsequent domestication of the horse did not sew the seeds of the state, which was actually done by those who migrated from the steppes after the last Ice Age to begin wet rice cultivation in alluvial valleys (for more, see James C Scott’s The Art of Not Being Governed). On the contrary, the new relationship between men and horses allowed nomadism to achieve a higher speed, which was necessary to evade the raiding-and-trading used by padi-states to secure the massive foreign labor needed for rice farming. This is why the nomad is “he who does not move” and not a migrant (A Thousand Plateaus, 381).
Accelerationism attempts to overcome the capitalist opposition of human and machine through the demand for full automation. As such, it peddles in technological Proudhonism that believes one can select what is good about technology and just delete what is bad. The Marxist retort is that development proceeds by its bad side. So instead of flashy things like self-driving cars, the real dot-communist question is: how will Amazon automate the tedious, low-paying jobs that computers are no good at? What happens to the data entry clerks, abusive-content managers, or help desk technicians? Until it figures out who will empty the recycle bin, accelerationism is only a socialism of the creative class.
The machinic is more than just machines–it approaches technology as a question of organization. The term is first used by Guattari in a 1968 paper titled “Machine and Structure” that he presented to Lacan’s Freudian School of Paris, a paper that would jumpstart his collaboration with Deleuze. He argues for favoring machine to structure. Structures transform parts of a whole by exchanging or substituting particularities so that every part shares in a general form (in other words, the production of isomorphism). An easy political example is the Leninist Party, which mediates the particularized private interests to form them into the general will of a class. Machines instead treat the relationship between things as a problem of communication. The result is the “control and communication” of Norbert Wiener’s cybernetics, which connects distinct things in a circuit instead of implanting a general logic. The word “machine” never really caught on but the concept has made inroads in the social sciences, where actor-network theory, game theory, behaviorism, systems theory, and other cybernetic approaches have gained acceptance.
Structure or machine, each engenders a different type of subjectivity, and each realizes a different model of communication. The two are found in A Thousand Plateaus, where Deleuze and Guattari note two different types of state subject formation: social subjection and machinic enslavement (456-460). While it only takes up a few short pages, the distinction is essential to Bernard Stiegler’s work and has been expertly elaborated by Maurizio Lazzarato in the book Signs and Machines. We are all familiar with molar social subjection synonymous with “agency”–it is the power that results from individuals bridging the gap between themselves and broader structures of representation, social roles, and institutional demands. This subjectivity is well outlined by Lacanians and other theorists of the linguistic turn (Virno, Rancière, Butler, Agamben). Missing from their accounts is machinic enslavement, which treats people as simply cogs in the machine. Such subjectivity is largely overlooked because it bypasses existential questions of recognition or self-identity. This is because machinic enslavement operates at the level of the infra-social or pre-individual through the molecular operators of unindividuated affects, sensations, desires not assigned to a subject. Offering a concrete example, Deleuze and Guattari reference Mumford’s megamachines of surplus societies that create huge landworks by treating humans as mere constituent parts. Capitalism revived the megamachine in the sixteenth century, and more recently, we have entered the “third age” of enslavement marked by the development of cybernetic and informational machines. In place of the pyramids are technical machines that use humans at places in technical circuits where computers are incapable or too costly, e.g. Amazon’s Mechanical Turk.
I should also clarify that not all machines are bad. Rather, Dark Deleuze only trusts one kind of machine, the war machine. And war machines follow a single trajectory–a line of flight out of this world. A major task of the war machine conveniently aligns with my politics of techno-anarchism: to blow apart the networks of communication created by the state.
Galloway: I can’t resist a silly pun, cannon of joy. Part of your project is about resisting a certain masculinist tendency. Is that a fair assessment? How do feminism and queer theory influence your project?
Culp: Feminism is hardwired into the tagline for Dark Deleuze through a critique of emotional labor and the exhibition of bodies–“A revolutionary Deleuze for today’s digital world of compulsory happiness, decentralized control, and overexposure.” The major thread I pull through the book is a materialist feminist one: something intolerable about this world is that it demands we participate in its accumulation and reproduction. So how about a different play on words: Sara Ahmed’s feminist killjoy, who refuses the sexual contract that requires women to appear outwardly grateful and agreeable? Or better yet, Joy Division? The name would associate the project with post-punk, its conceptual attack on the mainstream, and the band’s nod to the sexual labor depicted in the novella House of Dolls.
My critique of accumulation is also a media argument about connection. The most popular critics of ‘net culture are worried that we are losing ourselves. So on the one hand, we have Sherry Turkle who is worried that humans are becoming isolated in a state of being “alone-together”; and on the other, there is Bernard Stiegler, who thinks that the network supplants important parts of what it means to be human. I find this kind of critique socially conservative. It also victim-blames those who use social media the most. Recall the countless articles attacking women who take selfies as part of self-care regimen or teens who creatively evade parental authority. I’m more interested in the critique of early ’90s ‘net culture and its enthusiasm for the network. In general, I argue that network-centric approaches are now the dominant form of power. As such, I am much more interested in how the rhizome prefigures the digitally-coordinated networks of exploitation that have made Apple, Amazon, and Google into the world’s most powerful corporations. While not a feminist issue on its face, it’s easy to see feminism’s relevance when we consider the gendered division of labor that usually makes women the employees of choice for low-paying jobs in electronics manufacturing, call centers, and other digital industries.
Lastly, feminism and queer theory explicitly meet in my critique of reproduction. A key argument of Deleuze and Guattari in Anti-Oedipus is the auto-production of the real, which is to say, we already live in a “world without us.” My argument is that we need to learn how to hate some of the things it produces. Of course, this is a reworked critique of capitalist alienation and exploitation, which is a system that gives to us (goods and the wage) only because it already stole them behind our back (restriction from the means of subsistence and surplus value). Such ambivalence is the everyday reality of the maquiladora worker who needs her job but may secretly hope that all the factories burn to the ground. Such degrading feelings are the result of the compromises we make to reproduce ourselves. In the book, I give voice to them by fusing together David Halperin and Valerie Traub’s notion of gay shame acting as a solvent to whatever binds us to identity and Deleuze’s shame at not being able to prevent the intolerable. But feeling shame is not enough. To complete the argument, we need to draw out the queer feminist critique of reproduction latent in Marx and Freud. Détourning an old phrase: direct action begins at the point of reproduction. My first impulse is to rely on the punk rock attitude of Lee Edelman and Paul Preciado’s indictment of reproduction. But you are right that they have their masculinist moments, so what we need is something more post-punk–a little less aggressive and a lot more experimental. Hopefully Dark Deleuze is that.
Galloway: Edelman’s “fuck Annie” is one of the best lines in recent theory. “Fuck the social order and the Child in whose name we’re collectively terrorized; fuck Annie; fuck the waif from Les Mis; fuck the poor, innocent kid on the Net; fuck Laws both with capital ls and small; fuck the whole network of Symbolic relations and the future that serves as its prop” (No Future, 29). Your book claims, in essence, that the Fuck Annies are more interesting than the Aleatory Materialists. But how can we escape the long arm of Lucretius?
Culp: My feeling is that the politics of aleatory materialism remains ambiguous. Beyond the literal meaning of “joy,” there are important feminist takes on the materialist Spinoza of the encounter that deserve our attention. Isabelle Stengers’s work is among the most comprehensive, though the two most famous are probably Donna Haraway’s cyborg feminism and Karen Barad’s agential realism. Curiously, while New Materialism has been quite a boon for the art and design world, its socio-political stakes have never been more uncertain. One would hope that appeals to matter would lend philosophical credence to topical events such as #blacklivesmatter. Yet for many, New Materialism has simply led to a new formalism focused on material forms or realist accounts of physical systems meant to eclipse the “epistemological excesses” of post-structuralism. This divergence was not lost on commentators in the most recent issue of of October, which functioned as a sort of referendum on New Materialism. On the hand, the issue included a generous accounting of the many avenues artists have taken in exploring various “new materialist” directions. Of those, I most appreciated Mel Chen’s reminder that materialism cannot serve as a “get out of jail free card” on the history of racism, sexism, ablism, and speciesism. While on the other, it included the first sustained attack on New Materialism by fellow travelers. Certainly the New Materialist stance of seeing the world from the perspective of “real objects” can be valuable, but only if it does not exclude old materialism’s politics of labor. I draw from Deleuzian New Materialist feminists in my critique of accumulation and reproduction, but only after short-circuiting their world-building. This is a move I learned from Sue Ruddick, whose Theory, Culture & Society article on the affect of the philosopher’s scream is an absolute tour de force. And then there is Graham Burnett’s remark that recent materialisms are like “Etsy kissed by philosophy.” The phrase perfectly crystallizes the controversy, but it might be too hot to touch for at least a decade…
Galloway: Let’s focus more on the theme of affirmation and negation, since the tide seems to be changing. In recent years, a number of theorists have turned away from affirmation toward a different set of vectors such as negation, eclipse, extinction, or pessimism. Have we reached peak affirmation?
Culp: We should first nail down what affirmation means in this context. There is the metaphysical version of affirmation, such as Foucault’s proud title as a “happy positivist.” In this declaration in Archaeology of Knowledge and “The Order of Discourse,” he is not claiming to be a logical positivist. Rather, Foucault is distinguishing his approach from Sartrean totality, transcendentalism, and genetic origins (his secondary target being the reading-between-the-lines method of Althusserian symptomatic reading). He goes on to formalize this disagreement in his famous statement on the genealogical method, “Nietzsche, Genealogy, History.” Despite being an admirer of Sartre, Deleuze shares this affirmative metaphysics with Foucault, which commentators usually describe as an alternative to the Hegelian system of identity, contradiction, determinate negation, and sublation. Nothing about this “happily positivist” system forces us to be optimists. In fact, it only raises the stakes for locating how all the non-metaphysical senses of the negative persist.
Affirmation could be taken to imply a simple “more is better” logic as seen in Assemblage Theory and Latourian Compositionalism. Behind this logic is a principle of accumulation that lacks a theory of exploitation and fails to consider the power of disconnection. The Spinozist definition of joy does little to dispel this myth, but it is not like either project has revolutionary political aspirations. I think we would be better served to follow the currents of radical political developments over the last twenty years, which have been following an increasingly negative path. One part of the story is a history of failure. The February 15, 2003 global demonstration against the Iraq War was the largest protest in history but had no effect on the course of the war. More recently, the election of democratic socialist governments in Europe has done little to stave off austerity, even as economists publicly describe it as a bankrupt model destined to deepen the crisis. I actually find hope in the current circuit of struggle and think that its lack of alter-globalization world-building aspirations might be a plus. My cues come from the anarchist black bloc and those of the post-Occupy generation who would rather not pose any demands. This is why I return to the late Deleuze of the “control societies” essay and his advice to scramble the codes, to seek out spaces where nothing needs to be said, and to establish vacuoles of non-communication. Those actions feed the subterranean source of Dark Deleuze‘s darkness and the well from which comes hatred, cruelty, interruption, un-becoming, escape, cataclysm, and the destruction of worlds.
Galloway: Does hatred for the world do a similar work for you that judgment or moralism does in other writers? How do we avoid the more violent and corrosive forms of hate?
Culp: Writer Antonin Artaud’s attempt “to have done with the judgment of God” plays a crucial role in Dark Deleuze. Not just any specific authority but whatever gods are left. The easiest way to summarize this is “the three deaths.” Deleuze already makes note of these deaths in the preface to Difference and Repetition, but it only became clear to me after I read Gregg Flaxman’s Gilles Deleuze and the Fabulation of Philosophy. We all know of Nietzsche’s Death of God. With it, Nietzsche notes that God no longer serves as the central organizing principle for us moderns. Important to Dark Deleuze is Pierre Klossowski’s Nietzsche, who is part of a conspiracy against all of humanity. Why? Because even as God is dead, humanity has replaced him with itself. Next comes the Death of Man, which we can lay at the feet of Foucault. More than any other text, The Order of Things demonstrates how the birth of modern man was an invention doomed to fail. So if that death is already written in sand about to be washed away, then what comes next? Here I turn to the world, worlding, and world-building. It seems obvious when looking at the problems that plague our world: global climate change, integrated world capitalism, and other planet-scale catastrophes. We could try to deal with each problem one by one. But why not pose an even more radical proposition? What if we gave up on trying to save this world? We are already awash in sci-fi that tries to do this, though most of it is incredibly socially conservative. Perhaps now is the time for thinkers like us to catch up. Fragments of Deleuze already lay out the terms of the project. He ends the preface to Different and Repetition by assigning philosophy the task of writing apocalyptic science fiction. Deleuze’s book opens with lightning across the black sky and ends with the world swelling into a single ocean of excess. Dark Deleuze collects those moments and names it the Death of This World.
Galloway: Speaking of climate change, I’m reminded how ecological thinkers can be very religious, if not in word then in deed. Ecologists like to critique “nature” and tout their anti-essentialist credentials, while at the same time promulgating tellurian “change” as necessary, even beneficial. Have they simply replaced one irresistible force with another? But your “hatred of the world” follows a different logic…
Culp: Irresistible indeed! Yet it is very dangerous to let the earth have the final say. Not only does psychoanalysis teach us that it is necessary to buck the judgment of nature, the is/ought distinction at the philosophical core of most ethical thought refuses to let natural fact define the good. I introduce hatred to develop a critical distance from what is, and, as such, hatred is also a reclamation of the future in that it is a refusal to allow what-is to prevail over what-could-be. Such an orientation to the future is already in Deleuze and Guattari. What else is de-territorialization? I just give it a name. They have another name for what I call hatred: utopia.
Speaking of utopia, Deleuze and Guattari’s definition of utopia in What is Philosophy? as simultaneously now-here and no-where is often used by commentators to justify odd compromise positions with the present state of affairs. The immediate reference is Samuel Butler’s 1872 book Erewhon, a backward spelling of nowhere, which Deleuze also references across his other work. I would imagine most people would assume it is a utopian novel in the vein of Edward Bellamy’s Looking Backward. And Erewhon does borrow from the conventions of utopian literature, but only to skewer them with satire. A closer examination reveals that the book is really a jab at religion, Victorian values, and the British colonization of New Zealand! So if there is anything that the now-here of Erewhon has to contribute to utopia, it is that the present deserves our ruthless criticism. So instead of being a simultaneous now-here and no-where, hatred follows from Deleuze and Guattari’s suggestion in A Thousand Plateaus to “overthrow ontology” (25). Therefore, utopia is only found in Erewhon by taking leave of the now-here to get to no-where.
Galloway: In Dark Deleuze you talk about avoiding “the liberal trap of tolerance, compassion, and respect.” And you conclude by saying that the “greatest crime of joyousness is tolerance.” Can you explain what you mean, particularly for those who might value tolerance as a virtue?
Culp: Among the many followers of Deleuze today, there are a number of liberal Deleuzians. Perhaps the biggest stronghold is in political science, where there is a committed group of self-professed radical liberals. Another strain bridges Deleuze with the liberalism of John Rawls. I was a bit shocked to discover both of these approaches, but I suppose it was inevitable given liberalism’s ability to assimilate nearly any form of thought.
Herbert Marcuse recognized “repressive tolerance” as the incredible power of liberalism to justify the violence of positions clothed as neutral. The examples Marcuse cites are governments who say they respect democratic liberties because they allow political protest although they ignore protesters by labeling them a special interest group. For those of us who have seen university administrations calmly collect student demands, set up dead-end committees, and slap pictures of protestors on promotional materials as a badge of diversity, it should be no surprise that Marcuse dedicated the essay to his students. An important elaboration on repressive tolerance is Wendy Brown’s Regulating Aversion. She argues that imperialist US foreign policy drapes itself in tolerance discourse. This helps diagnose why liberal feminist groups lined up behind the US invasion of Afghanistan (the Taliban is patriarchal) and explains how a mere utterance of ISIS inspires even the most progressive liberals to support outrageous war budgets.
Because of their commitment to democracy, Brown and Marcuse can only qualify liberalism’s universal procedures for an ethical subject. Each criticizes certain uses of tolerance but does not want to dispense with it completely. Deleuze’s hatred of democracy makes it much easier for me. Instead, I embrace the perspective of a communist partisan because communists fight from a different structural position than that of the capitalist.
Galloway: Speaking of structure and position, you have a section in the book on asymmetry. Most authors avoid asymmetry, instead favoring concepts like exchange or reciprocity. I’m thinking of texts on “the encounter” or “the gift,” not to mention dialectics itself as a system of exchange. Still you want to embrace irreversibility, incommensurability, and formal inoperability–why?
Culp: There are a lot of reasons to prefer asymmetry, but for me, it comes down to a question of political strategy.
First, a little background. Deleuze and Guattari’s critique of exchange is important to Anti-Oedipus, which was staged through a challenge to Claude Lévi-Strauss. This is why they shift from the traditional Marxist analysis of mode of production to an anthropological study of anti-production, for which they use the work of Pierre Clastres and Georges Bataille to outline non-economic forms of power that prevented the emergence of capitalism. Contemporary anthropologists have renewed this line of inquiry, for instance, Eduardo Viveiros de Castro, who argues in Cannibal Metaphysics that cosmologies differ radically enough between peoples that they essentially live in different worlds. The cannibal, he shows, is not the subject of a mode of production but a mode of predation.
Those are not the stakes that interest me the most. Consider instead the consequence of ethical systems built on the gift and political systems of incommensurability. The ethical approach is exemplified by Derrida, whose responsibility to the other draws from the liberal theological tradition of accepting the stranger. While there is distance between self and other, it is a difference that is bridged through the democratic project of radical inclusion, even if such incorporation can only be aporetically described as a necessary-impossibility. In contrast, the politics of asymmetry uses incommensurability to widen the chasm opened by difference. It offers a strategy for generating antagonism without the formal equivalence of dialectics and provides an image of revolution based on fundamental transformation. The former can be seen in the inherent difference between the perspective of labor and the perspective of capital, whereas the latter is a way out of what Guy Debord calls “a perpetual present.”
Galloway: You are exploring a “dark” Deleuze, and I’m reminded how the concepts of darkness and blackness have expanded and interwoven in recent years in everything from afro-pessimism to black metal theory (which we know is frighteningly white). How do you differentiate between darkness and blackness? Or perhaps that’s not the point?
Culp: The writing on Deleuze and race is uneven. A lot of it can be blamed on the imprecise definition of becoming. The most vulgar version of becoming is embodied by neoliberal subjects who undergo an always-incomplete process of coming more into being (finding themselves, identifying their capacities, commanding their abilities). The molecular version is a bit better in that it theorizes subjectivity as developing outside of or in tension with identity. Yet the prominent uses of becoming and race rarely escaped the postmodern orbit of hybridity, difference, and inclusive disjunction–the White Man’s face as master signifier, miscegenation as anti-racist practice, “I am all the names of history.” You are right to mention afro-pessimism, as it cuts a new way through the problem. As I’ve written elsewhere, Frantz Fanon describes being caught between “infinity and nothingness” in his famous chapter on the fact of blackness in Black Skin White Masks. The position of infinity is best championed by Fred Moten, whose black fugitive is the effect of an excessive vitality that has survived five hundred years of captivity. He catches fleeting moments of it in performances of jazz, art, and poetry. This position fits well with the familiar figures of Deleuzo-Guattarian politics: the itinerant nomad, the foreigner speaking in a minor tongue, the virtuoso trapped in-between lands. In short: the bastard combination of two or more distinct worlds. In contrast, afro-pessimism is not the opposite of the black radical tradition but its outside. According to afro-pessimism, the definition of blackness is nothing but the social death of captivity. Remember the scene of subjection mentioned by Fanon? During that nauseating moment he is assailed by a whole series of cultural associations attached to him by strangers on the street. “I was battered down by tom-toms, cannibalism, intellectual deficiency, fetishism, racial defects, slave-ships, and above all else, above all: ‘Sho’ good eatin”” (112). The lesson that afro-pessimism draws from this scene is that cultural representations of blackness only reflect back the interior of white civil society. The conclusion is that combining social death with a culture of resistance, such as the one embodied by Fanon’s mentor Aimé Césaire, is a trap that leads only back to whiteness. Afro-pessimism thus follows the alternate route of darkness. It casts a line to the outside through an un-becoming that dissolves the identity we are give as a token for the shame of being a survivor.
Galloway: In a recent interview the filmmaker Haile Gerima spoke about whiteness as “realization.” By this he meant both realization as such–self-realization, the realization of the self, the ability to realize the self–but also the more nefarious version as “realization through the other.” What’s astounding is that one can replace “through” with almost any other preposition–for, against, with, without, etc.–and the dynamic still holds. Whiteness is the thing that turns everything else, including black bodies, into fodder for its own realization. Is this why you turn away from realization toward something like profanation? And is darkness just another kind of whiteness?
Culp: Perhaps blackness is to the profane as darkness is to the outside. What is black metal if not a project of political-aesthetic profanation? But as other commentators have pointed out, the politics of black metal is ultimately telluric (e.g. Benjamin Noys’s “‘Remain True to the Earth!’: Remarks on the Politics of Black Metal”). The left wing of black metal is anarchist anti-civ and the right is fascist-nativist. Both trace authority back to the earth that they treat as an ultimate judge usurped by false idols.
The process follows what Badiou calls “the passion for the real,” his diagnosis of the Twentieth Century’s obsession with true identity, false copies, and inauthentic fakes. His critique equally applies to Deleuzian realists. This is why I think it is essential to return to Deleuze’s work on cinema and the powers of the false. One key example is Orson Welles’s F for Fake. Yet my favorite is the noir novel, which he praises in “The Philosophy of Crime Novels.” The noir protagonist never follows in the footsteps of Sherlock Holmes or other classical detectives’s search for the real, which happens by sniffing out the truth through a scientific attunement of the senses. Rather, the dirty streets lead the detective down enough dead ends that he proceeds by way of a series of errors. What noir reveals is that crime and the police have “nothing to do with a metaphysical or scientific search for truth” (82). The truth is rarely decisive in noir because breakthroughs only come by way of “the great trinity of falsehood”: informant-corruption-torture. The ultimate gift of noir is a new vision of the world whereby honest people are just dupes of the police because society is fueled by falsehood all the way down.
To specify the descent to darkness, I use darkness to signify the outside. The outside has many names: the contingent, the void, the unexpected, the accidental, the crack-up, the catastrophe. The dominant affects associated with it are anticipation, foreboding, and terror. To give a few examples, H. P. Lovecraft’s scariest monsters are those so alien that characters cannot describe them with any clarity, Maurice Blanchot’s disaster is the Holocaust as well as any other event so terrible that it interrupts thinking, and Don DeLillo’s “airborne toxic event” is an incident so foreign that it can only be described in the most banal terms. Of Deleuze and Guattari’s many different bodies without organs, one of the conservative varieties comes from a Freudian model of the psyche as a shell meant to protect the ego from outside perturbations. We all have these protective barriers made up of habits that help us navigate an uncertain world–that is the purpose of Guattari’s ritornello, that little ditty we whistle to remind us of the familiar even when we travel to strange lands. There are two parts that work together, the refrain and the strange land. The refrains have only grown yet the journeys seem to have ended.
I’ll end with an example close to my own heart. Deleuze and Guattari are being used to support new anarchist “pre-figurative politics,” which is defined as seeking to build a new society within the constraints of the now. The consequence is that the political horizon of the future gets collapsed into the present. This is frustrating for someone like me, who holds out hope for a revolutionary future that ceases the million tiny humiliations that make up everyday life. I like J. K. Gibson-Graham’s feminist critique of political economy, but community currencies, labor time banks, and worker’s coops are not my image of communism. This is why I have drawn on the gothic for inspiration. A revolution that emerges from the darkness holds the apocalyptic potential of ending the world as we know it.
Works Cited
- Ahmed, Sara. The Promise of Happiness. Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 2010.
- Artaud, Antonin. To Have Done With The Judgment of God. 1947. Live play, Boston: Exploding Envelope, c1985. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VHtrY1UtwNs.
- Badiou, Alain. The Century. 2005. Cambridge, UK: Polity Press, 2007.
- Barad, Karen. Meeting the Universe Halfway: Quantum Physics and the Entanglement of Matter. Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 2007.
- Bataille, Georges. “The Notion of Expenditure.” 1933. In Visions of Excess: Selected Writings, 1927-1939, translated by Allan Stoekl, Carl R. Lovin, and Donald M. Leslie Jr., 167-81. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1985.
- Bellamy, Edward. Looking Backward: From 2000 to 1887. Boston: Ticknor & co., 1888.
- Blanchot, Maurice. The Writing of the Disaster. 1980. Translated by Ann Smock. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press, 1995.
- Brown, Wendy. Regulating Aversion: Tolerance in the Age of Identity and Empire. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 2006.
- Burnett, Graham. “A Questionnaire on Materialisms.” October 155 (2016): 19-20.
- Butler, Samuel. Erewhon: or, Over the Range. 1872. London: A.C. Fifield, 1910. http://www.gutenberg.org/files/1906/1906-h/1906-h.htm.
- Chen, Mel Y. “A Questionnaire on Materialisms.” October 155 (2016): 21-22.
- Clastres, Pierre. Society against the State. 1974. Translated by Robert Hurley and Abe Stein. New York: Zone Books, 1987.
- Culp, Andrew. Dark Deleuze. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 2016.
- ———. “Blackness.” New York: Hostis, 2015.
- Debord, Guy. The Society of the Spectacle. 1967. Translated by Fredy Perlman et al. Detroit: Red and Black, 1977.
- DeLanda, Manuel. A Thousand Years of Nonlinear History. New York: Zone Books, 2000.
- ———. War in the Age of Intelligent Machines. New York: Zone Books, 1991.
- DeLillo, Don. White Noise. New York: Viking Press, 1985.
- Deleuze, Gilles. Cinema 2: The Time-Image. 1985. Translated by Hugh Tomlinson and Robert Galeta. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1989.
- ———. “The Philosophy of Crime Novels.” 1966. Translated by Michael Taormina. In Desert Islands and Other Texts, 1953-1974, 80-85. New York: Semiotext(e), 2004.
- ———. Difference and Repetition. 1968. Translated by Paul Patton. New York: Columbia University Press, 1994.
- ———. Empiricism and Subjectivity: An Essay on Hume’s Theory of Human Nature. 1953. Translated by Constantin V. Boundas. New York: Columbia University Press, 1995.
- ———. Foucault. 1986. Translated by Seán Hand. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1988.
- Deleuze, Gilles, and Félix Guattari. Anti-Oedipus. 1972. Translated by Robert Hurley, Mark Seem, and Helen R. Lane. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1977.
- ———. A Thousand Plateaus. 1980. Translated by Brian Massumi. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1987.
- ———. What Is Philosophy? 1991. Translated by Hugh Tomlinson and Graham Burchell. New York: Columbia University Press, 1994.
- Derrida, Jacques. The Gift of Death and Literature in Secret. Translated by David Willis. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2007; second edition.
- Edelman, Lee. No Future: Queer Theory and the Death Drive. Durham, N.C.: Duke University Press, 2004.
- Fanon, Frantz. Black Skin White Masks. 1952. Translated by Charles Lam Markmann. New York: Grove Press, 1968.
- Flaxman, Gregory. Gilles Deleuze and the Fabulation of Philosophy. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 2011.
- Foucault, Michel. The Archaeology of Knowledge and the Discourse on Language. 1971. Translated by A.M. Sheridan Smith. New York: Pantheon Books, 1972.
- ———. “Nietzsche, Genealogy, History.” 1971. In Language, Counter-Memory, Practice: Selected Essays and Interviews, translated by Donald F. Bouchard and Sherry Simon, 113-38. Ithaca, N.Y.: Cornell University Press, 1977.
- ———. The Order of Things. 1966. New York: Pantheon Books, 1970.
- Freud, Sigmund. Beyond the Pleasure Principle. 1920. Translated by James Strachley. London: Hogarth Press, 1955.
- ———. “Instincts and their Vicissitudes.” 1915. Translated by James Strachley. In Standard Edition of the Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud 14, 111-140. London: Hogarth Press, 1957.
- Gerima, Haile. “Love Visual: A Conversation with Haile Gerima.” Interview by Sarah Lewis and Dagmawi Woubshet. Aperture, Feb 23, 2016. http://aperture.org/blog/love-visual-haile-gerima/.
- Gibson-Graham, J.K. The End of Capitalism (As We Knew It): A Feminist Critique of Political Economy. Hoboken: Blackwell, 1996.
- ———. A Postcapitalist Politics. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 2006.
- Guattari, Félix. “Machine and Structure.” 1968. Translated by Rosemary Sheed. In Molecular Revolution: Psychiatry and Politics, 111-119. Harmondsworth, Middlesex: Penguin, 1984.
- Halperin, David, and Valerie Traub. “Beyond Gay Pride.” In Gay Shame, 3-40. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2009.
- Haraway, Donna. Simians, Cyborgs, and Women: The Reinvention of Nature. New York: Routledge, 1991.
- Klossowski, Pierre. “Circulus Vitiosus.” Translated by Joseph Kuzma. The Agonist: A Nietzsche Circle Journal 2, no. 1 (2009): 31-47.
- ———. Nietzsche and the Vicious Circle. 1969. Translated by Daniel W. Smith. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1997.
- Lazzarato, Maurizio. Signs and Machines. 2010. Translated by Joshua David Jordan. Los Angeles: Semiotext(e), 2014.
- Marcuse, Herbert. “Repressive Tolerance.” In A Critique of Pure Tolerance, 81-117. Boston: Beacon Press, 1965.
- Mauss, Marcel. The Gift: The Form and Reason for Exchange in Archaic Societies. 1950. Translated by W. D. Hallis. New York: Routledge, 1990.
- Moten, Fred. In The Break: The Aesthetics of the Black Radical Tradition. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 2003.
- Mumford, Lewis. Technics and Human Development. San Diego: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, 1967.
- Noys, Benjamin. “‘Remain True to the Earth!’: Remarks on the Politics of Black Metal.” In: Hideous Gnosis: Black Metal Theory Symposium 1 (2010): 105-128.
- Preciado, Paul. Testo-Junkie: Sex, Drugs, and Biopolitics in the Phamacopornographic Era. 2008. Translated by Bruce Benderson. New York: The Feminist Press, 2013.
- Ruddick, Susan. “The Politics of Affect: Spinoza in the Work of Negri and Deleuze.” Theory, Culture, Society 27, no. 4 (2010): 21-45.
- Scott, James C. The Art of Not Being Governed: An Anarchist History of Upland Southeast Asia. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2009.
- Sexton, Jared. “Afro-Pessimism: The Unclear Word.” In Rhizomes 29 (2016). http://www.rhizomes.net/issue29/sexton.html.
- ———. “Ante-Anti-Blackness: Afterthoughts.” In Lateral 1 (2012). http://lateral.culturalstudiesassociation.org/issue1/content/sexton.html.
- ———. “The Social Life of Social Death: On Afro-Pessimism and Black Optimism.” In Intensions 5 (2011). http://www.yorku.ca/intent/issue5/articles/jaredsexton.php.
- Stiegler, Bernard. For a New Critique of Political Economy. Cambridge: Polity Press, 2010.
- ———. Technics and Time 1: The Fault of Epimetheus. 1994. Translated by George Collins and Richard Beardsworth. Redwood City, CA: Stanford University Press, 1998.
- Tiqqun. “How Is It to Be Done?” 2001. In Introduction to Civil War. 2001. Translated by Alexander R. Galloway and Jason E. Smith. Los Angeles, Calif.: Semiotext(e), 2010.
- Toynbee, Arnold. A Study of History. Abridgement of Volumes I-VI by D.C. Somervell. London, Oxford University Press, 1946.
- Turkle, Sherry. Alone Together: Why We Expect More from Technology and Less from Each Other. New York: Basic Books, 2012.
- Viveiros de Castro, Eduardo. Cannibal Metaphysics: For a Post-structural Anthropology. 2009. Translated by Peter Skafish. Minneapolis, Minn.: Univocal, 2014.
- Villani, Arnaud. La guêpe et l’orchidée. Essai sur Gilles Deleuze. Paris: Éditions de Belin, 1999.
- Welles, Orson, dir. F for Fake. 1974. New York: Criterion Collection, 2005.
- Wiener, Norbert. Cybernetics: Cybernetics: Or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1948; second revised edition.
- Williams, Alex, and Nick Srincek. “#ACCELERATE MANIFESTO for an Accelerationist Politics.” Critical Legal Thinking. 2013. http://criticallegalthinking.com/2013/05/14/accelerate-manifesto-for-an-accelerationist-politics/.
Alexander R. Galloway is a writer and computer programer working on issues in philosophy, technology, and theories of mediation. Professor of Media, Culture, and Communication at New York University, he is author of several books and dozens of articles on digital media and critical theory, including Protocol: How Control Exists after Decentralization (MIT, 2006), Gaming: Essays in Algorithmic Culture (University of Minnesota, 2006); The Interface Effect (Polity, 2012), and most recently Laruelle: Against the Digital (University of Minnesota, 2014), reviewed here in 2014. He is a frequent contributor to The b2 Review “Digital Studies.”
Andrew Culp is a Visiting Assistant Professor of Rhetoric Studies at Whitman College. He specializes in cultural-communicative theories of power, the politics of emerging media, and gendered responses to urbanization. His work has appeared in Radical Philosophy, Angelaki, Affinities, and other venues. He previously pre-reviewed Galloway’s Laruelle: Against the Digital for The b2 Review “Digital Studies.”







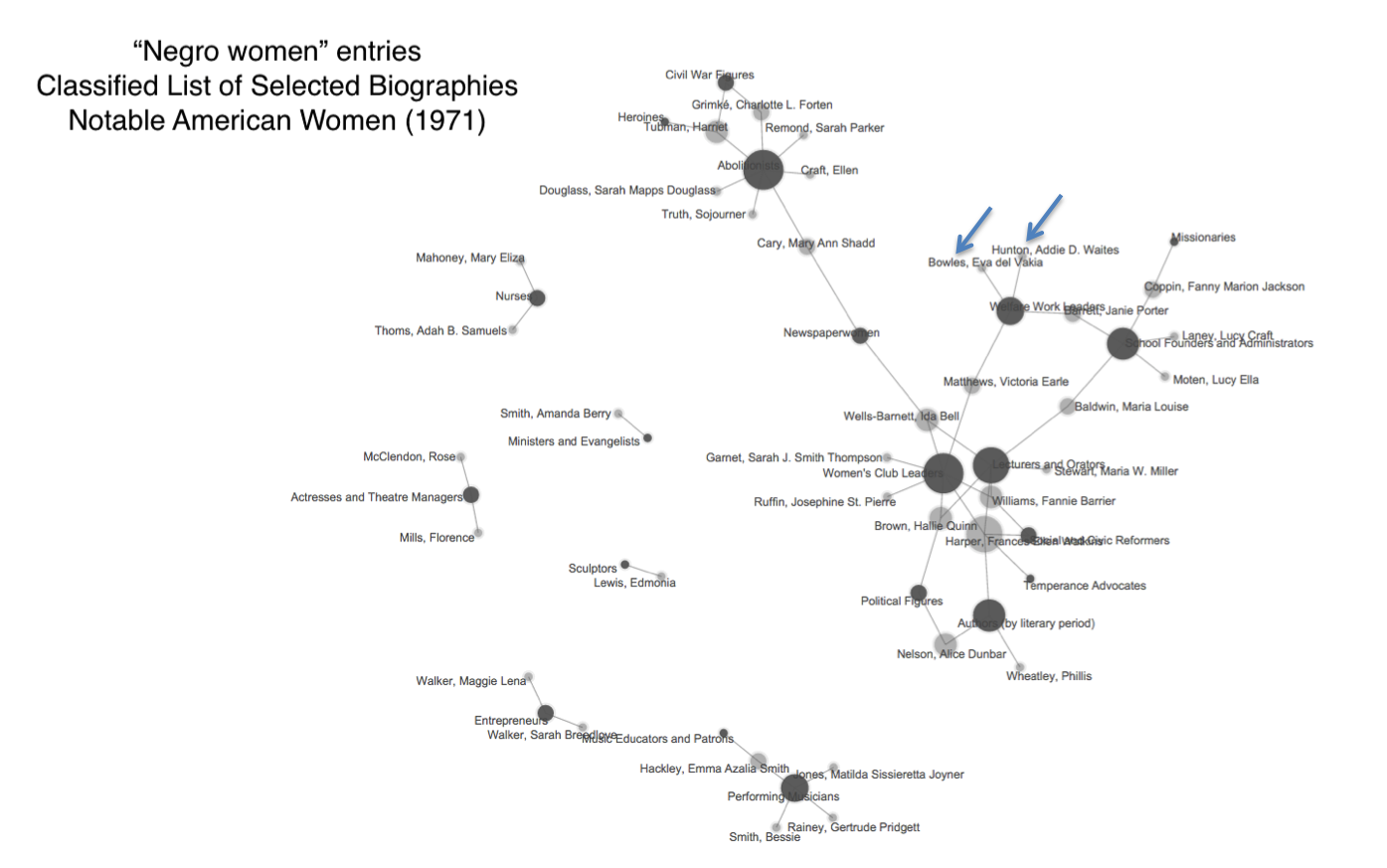
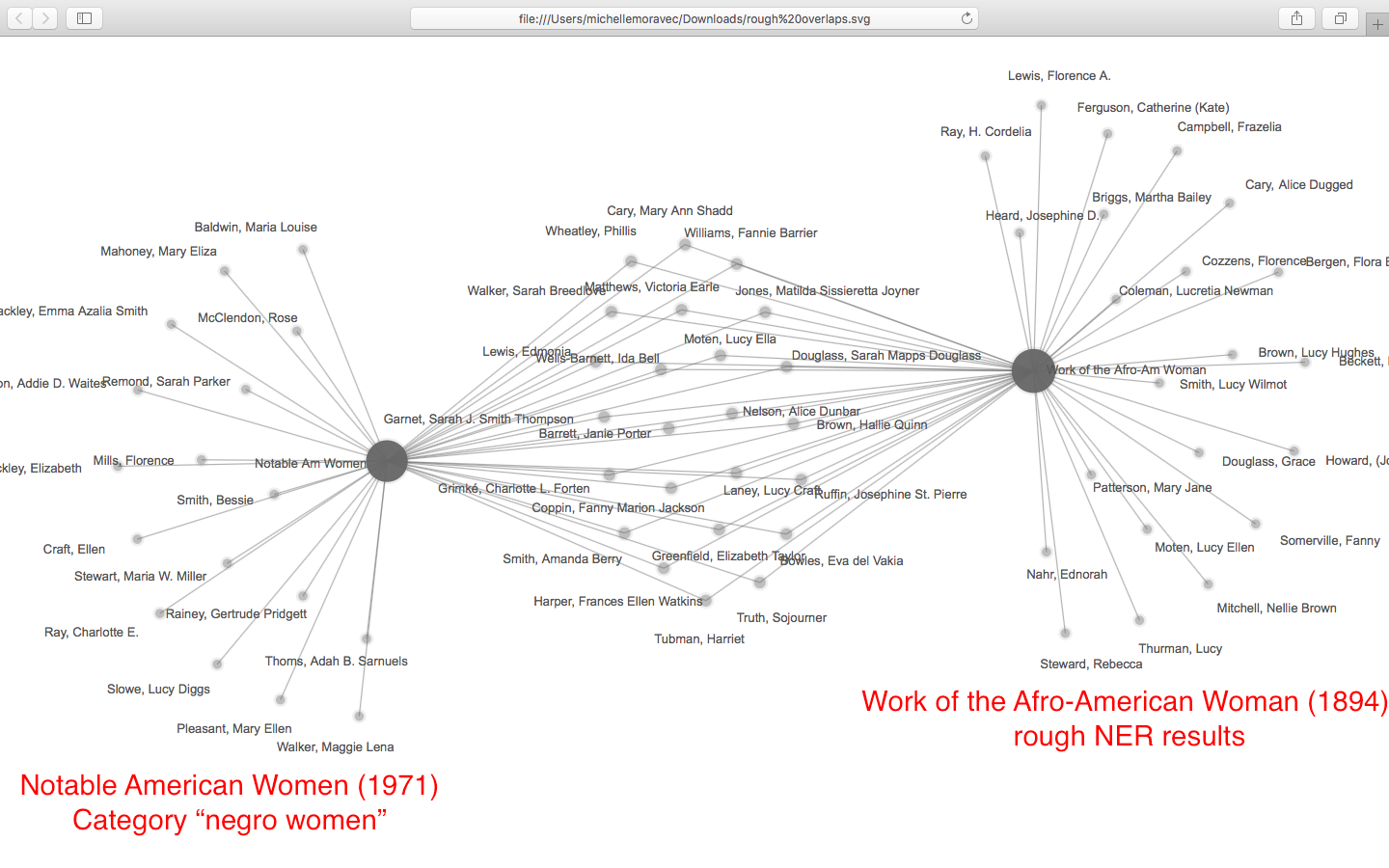
 As this poetic quote by Sarah Josepha Hale, nineteenth-century author and influential editor reminds us, context is everything. The challenge, if we wish to write women back into history via Wikipedia, is to figure out how to shift the frame of references so that our stars can shine, since the problem of who precisely is “worthy of commemoration” or in Wikipedia language, who is deemed
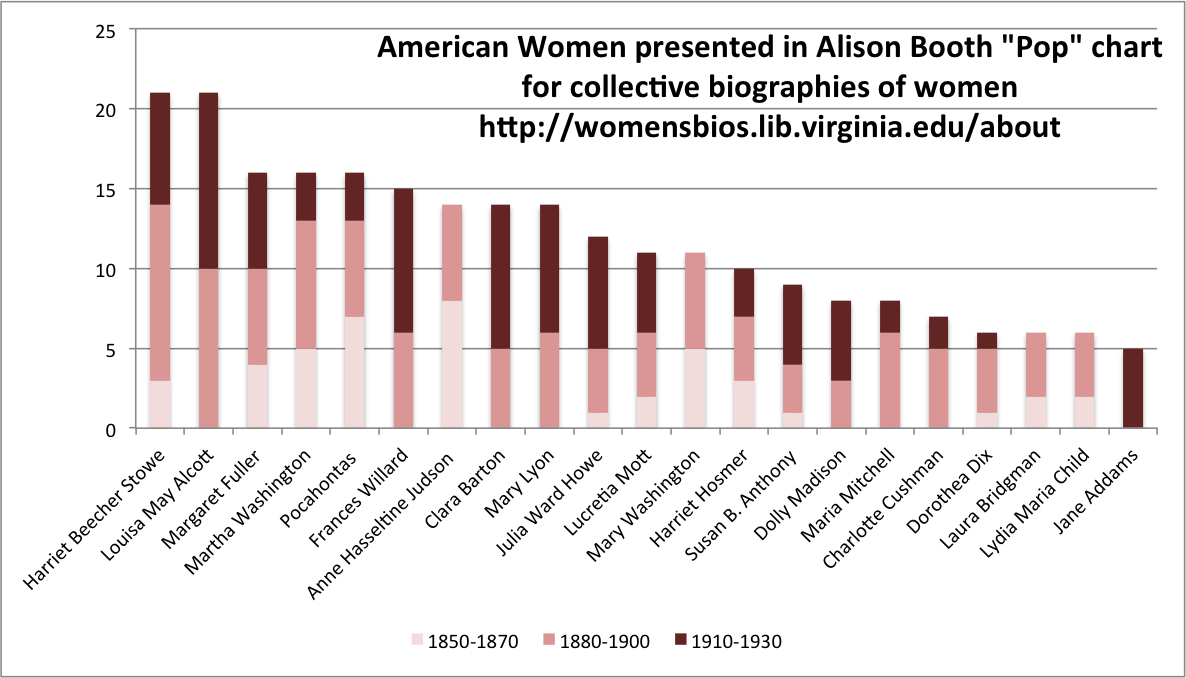
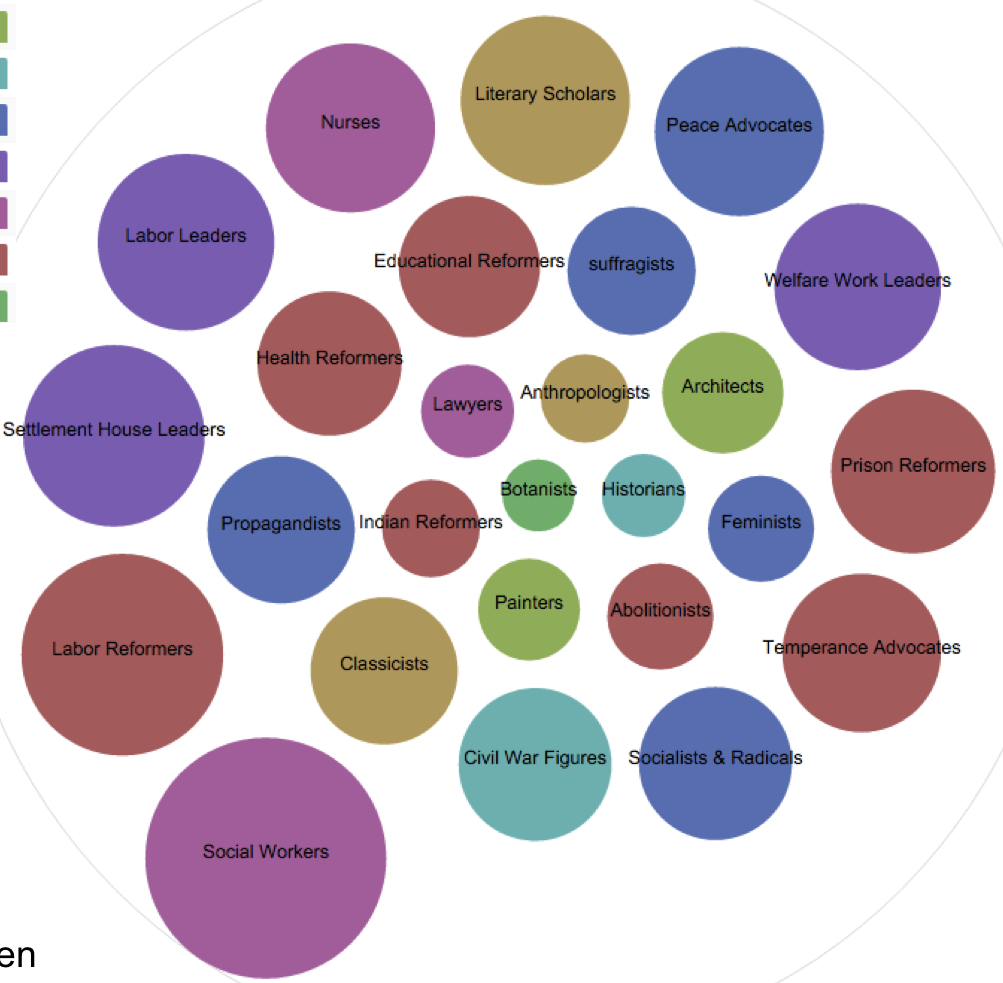
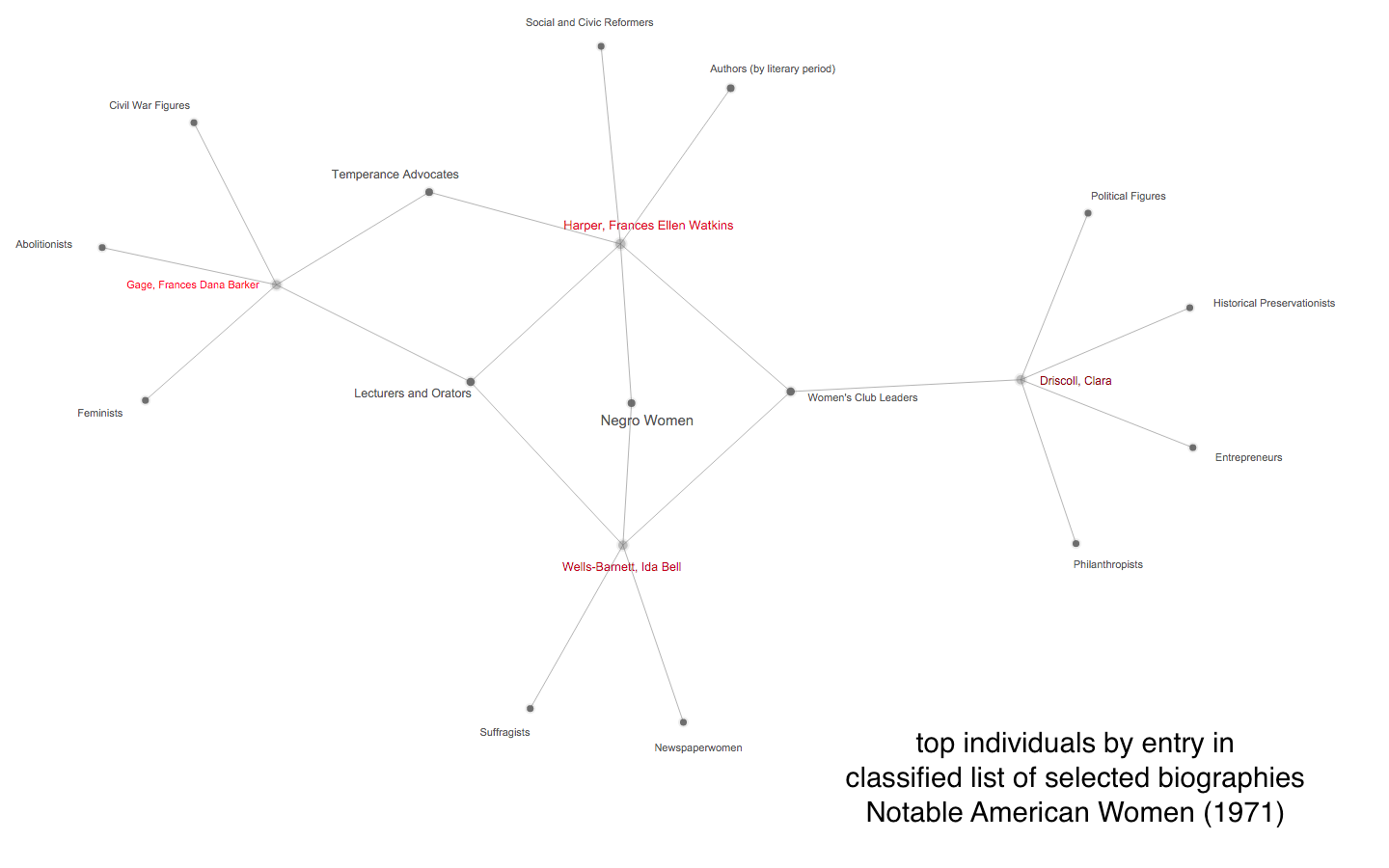
As this poetic quote by Sarah Josepha Hale, nineteenth-century author and influential editor reminds us, context is everything. The challenge, if we wish to write women back into history via Wikipedia, is to figure out how to shift the frame of references so that our stars can shine, since the problem of who precisely is “worthy of commemoration” or in Wikipedia language, who is deemed  mes of prosopography published during what might be termed the heyday of the genre, 1830-1940, when the rise of the middle class and increased literacy combined with relatively cheap production of books to make such volumes both practicable and popular. Booth also points out, that lest we consign the genre to the realm of mere curiosity, predating the invention of “women’s history” the compilers, editrixes or authors of these volumes considered them a contribution to “national history” and indeed Booth concludes that the volumes were “indispensable aids in the formation of nationhood.”
mes of prosopography published during what might be termed the heyday of the genre, 1830-1940, when the rise of the middle class and increased literacy combined with relatively cheap production of books to make such volumes both practicable and popular. Booth also points out, that lest we consign the genre to the realm of mere curiosity, predating the invention of “women’s history” the compilers, editrixes or authors of these volumes considered them a contribution to “national history” and indeed Booth concludes that the volumes were “indispensable aids in the formation of nationhood.”